- 30
- Oct
Causes of harmonics in induction melting furnaces
Causes of harmonics in induction melting furnaces
The main circuit of the induction melting furnace can use three-phase 6-pulse or six-phase 12-pulse. The purpose of using 12-pulse rectification is to reduce high-order harmonics. Because the transformer uses the △/¥ connection, the 5th and 7th Harmonic currents cancel each other out in the transformer, leaving very small 11th and 13th harmonics. If the grid capacity is large enough, it can meet the requirements of the national standard (GB/T 14549—1993). Therefore, harmonics may not be considered in this case. The problem of wave treatment: If the grid capacity is relatively small, the nonlinear load capacity is large, and the harmonics seriously affect the power supply system, then the harmonic treatment needs to be considered.
Harmonics are multiples of the main power grid frequency (50Hz). Through Fourier transform, a non-sinusoidal function can be decomposed into multiple sine-functional harmonic components, that is, non-sinusoidal signals can be decomposed into basic parts and sums by Fourier transform. Its multiple, the waveform on the outside of the sine frequency is known as the fundamental component, and it responds at the frequency. The above waveform is called the harmonic component, and its multiples are called the 3rd, 5th, 7th, 11th, 13th and other harmonic components. The schematic diagram of various harmonic characteristics is shown in Figure 2-15.
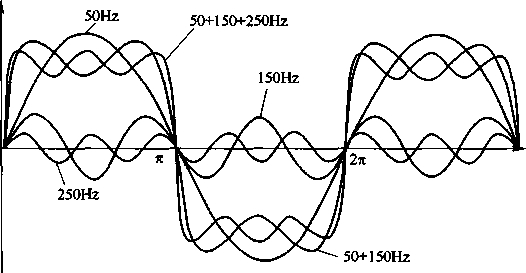
Figure 2-15 Schematic diagram of multiple harmonic characteristics
