- 13
- Oct
Induction heating furnace for heating steel strip
Induction heating furnace for heating steel strip

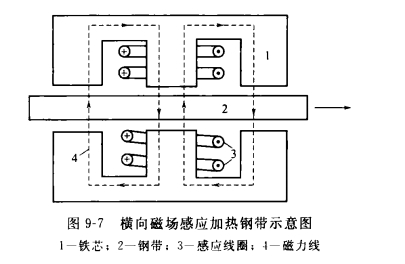
A schematic diagram of a transverse magnetic field induction heating furnace heating a steel strip. The inductor for heating the steel strip consists of an iron core and a coil. The inductor is composed of upper and lower parts. When the variable-frequency current is passed through the coil, there is an alternating magnetic field in the gap between the upper and lower induction coils. The magnetic field lines of the magnetic field pass through the steel strip perpendicularly, heating the steel strip to a predetermined temperature. Since the lines of magnetic force pass through the steel strip transversely, they are called transverse magnetic fields to distinguish them from longitudinal magnetic fields.
It can be seen from the structure of the inductor that the inductor for transverse magnetic field heating is far more complicated than that for longitudinal magnetic field heating. As the heating power increases, the structure of the transverse magnetic field heating inductor becomes more complicated. This is the equipment problem of the transverse magnetic field induction heating furnace.
The characteristics of the strip transverse magnetic field induction heating furnace
Comparing the two magnetic field induction heating furnace methods, it can be concluded that when the transverse magnetic field heats the steel strip or sheet, it has the characteristics of high heating electric efficiency, low power frequency, fast heating speed, and poor temperature uniformity.
