- 17
- Oct
Description of spiral inductor structure of induction heating furnace
Description of spiral inductor structure of induction heating furnace
The spiral inductor of induction heating furnace is one of the most used intermediate frequency inductors, which can be used to heat round steel and round bars with round, square or rectangular cross-sections.
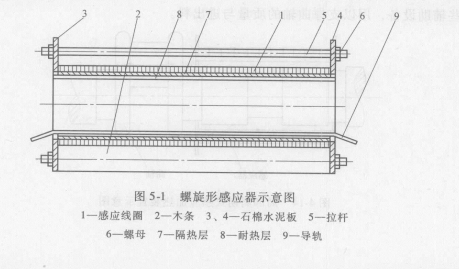
(1) Figure 5-1 is a spiral inductor for heating cylindrical, round steel, and round bars. The induction coil 1 is made of square or rectangular pure copper tubes, and the coil is supported by longitudinal wooden bars 2. The two ends of the wooden strips are fastened to the asbestos cement boards 3 and 4 with screws. In order to make the whole sensor have the necessary rigidity, four tie rods 5 are used to pull two asbestos cement boards, and nuts 6 are used to tighten them. The heat-insulating layer 7 is used to improve the thermal efficiency; the heat-resistant layer 8 is used to protect the heat-insulating layer from being burnt; the guide rail 9 is used to support the round steel and the round rod, and guide the round steel and the round rod to be fed. The guide rail is welded from a flat strip of non-magnetic steel to a pipe, and is cooled by water when heated. The thickness of the flat strip should be no less than 3 ~ 4mm, and the diameter of the tube is usually 15-20mm. On the coil 1, in order to change the length of the coil and adjust the number of turns of the coil, a tap is reserved. There is a wiring board at the end of the coil for connection with the power bus.
There are three treatment methods for the insulation between the turns of the coil of the induction heating furnace.
1) A non-alkali glass ribbon is wrapped around the pure copper tube, and it is varnished and dried.
2) Use 1mm thick insulating plates to make washers according to the inner and outer dimensions of the induction coil, and cut the insulating washers in the radial direction. The number of insulating washers is one less than the number of turns of the induction coil. Insert these insulating washers between the turns of the coil to form a continuous spiral surface. In this way, the pure copper tube of the coil does not need to be wrapped with an insulating layer.
3) Use air insulation, that is, to open the turns of the induction coil, leaving a gap of 2-4mm. The size of this gap depends on the width of the pure copper tube of the coil. The insulation coefficient between the turns of the induction coil should be made.
g = B/S = 0. 8 – 0.92
Where B-the width of the pure copper tube (mm);
S——The pitch of the induction coil (mm).
When the inductor of the induction heating furnace is very long or the number of turns of the induction coil is large, use a water circuit for cooling, and only under high enough water pressure can the necessary amount of water flow in the pure copper pipe. However, the pressure of tap water in the factory is generally (1.5-2) 105Pa. To ensure the cooling of the coil, the induction coil can be divided into several sections, and each section can be connected in parallel for water supply.
In order to protect the induction coil from being burnt out by the heated round steel and rod, the coil is equipped with a heat-insulating layer and a heat-resistant layer. On the one hand, the function of the heat insulation layer is to keep warm, but also to reduce the heat transfer to the coil. The insulation material and its thickness are determined according to the heating temperature of the round steel and the round rod. High silica glass wool and aluminum silicate fiber felt can be used, and the thickness is about 5 ~ 15mm. The heat-resistant layer is made of refractory material, and it depends on the actual use. When the heating temperature of round steel and round rod is below 1000℃, the bush can be made of non-magnetic stainless steel plate; when round steel, the heating temperature of round rod When the temperature exceeds 1000℃, it must be made of refractory materials such as ceramics, such as corundum or silicon carbide materials, which have better resistance to rapid cooling and heating, but the thermal conductivity of silicon carbide materials is higher, and the heat transfer loss will be greater.
