- 22
- Sep
The service life of ladle breathable bricks and nozzle block bricks
The service life of ladle breathable bricks and nozzle block bricks
The ladle is an important thermal equipment for steel-making manufacturers. It uses bottom-blown argon-breathable bricks to complete the goal of refining molten steel. The function of the ladle lining is to protect the metal structure of the ladle shell from the high temperature of molten steel, and to keep the molten steel in the ladle for a certain period of time to adjust the temperature of the molten steel, fine-tune and uniform chemical composition, and eliminate metal inclusions in the molten steel. And harmful gases.
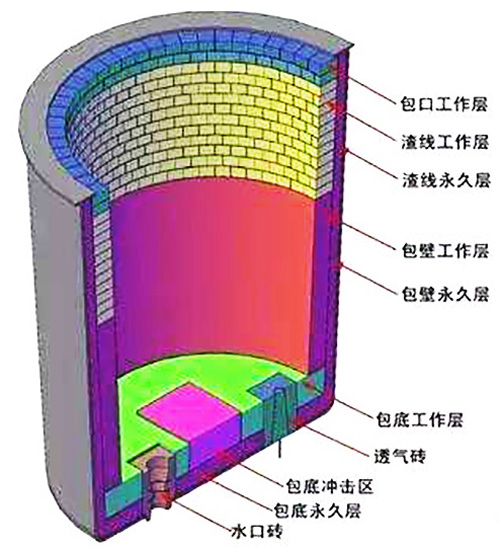
(Picture) Ladle lining
The main damages to the inner lining of the ladle working layer are: erosion, spalling, erosion and hydration.
Erosion: The molten steel flowing over the surface of the refractory material will cause physical wear. The molten steel will have a greater impact on the sliding plate mechanism, the nozzle seat brick and the part of the breathable brick beyond the bottom of the bag.
Spalling: The refractory material is subjected to rapid cooling and heating to generate stress. When the stress is too large and exceeds the strength of the refractory material, cracks will occur inside the refractory material. With the expansion of the crack area and traffic, the surface of the refractory material will be peeled off to a greater extent or even completely.
Erosion: There are two main types of erosion. One is reaction with iron oxide or acidic substances (such as silica) in the slag, and the reaction causes the ladle lining to become molten slag, which leads to the damage of refractory materials; the other is refractory Corrosion caused by the reaction of carbon in bricks with iron oxide or oxygen in the air. These two types of reactions can cause the internal structure of the refractory brick to become loose and the strength to decrease, and eventually cause the refractory brick lining to be eroded by molten slag or molten steel.
Hydration: The water in the ladle lining before and during baking reacts with the magnesium oxide in the magnesia carbon brick to hydrate. After hydration, the permeability to steel slag and molten steel is very poor, the physical and chemical properties are much worse than before, and the erosion of the ladle lining will become faster and faster.

