- 01
- Oct
Hot blast stove checker brick
Hot blast stove checker brick
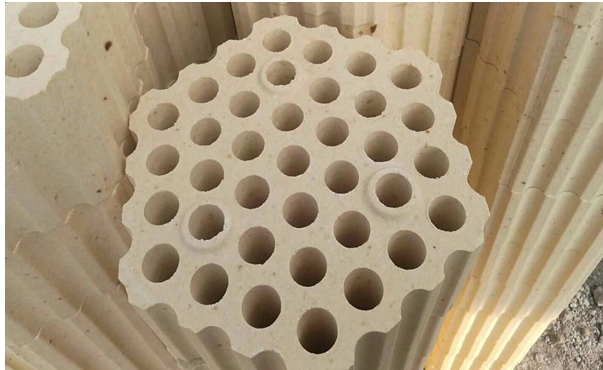
A. The heat carrier of the hot blast stove is a porous checker brick. The porous checker brick is currently widely recognized and accepted by the world’s ironmaking industry. It has strong heat exchange capacity, large heat storage area, smooth ventilation, and low resistance. Characteristic heat-carrying heat storage body. …
B. Checker brick is a kind of refractory brick commonly used in hot blast stoves. Its surface is uneven, with transparent holes in the middle. According to its structural characteristics, the commonly used porous check bricks are mainly: 7 holes, 19 holes, 31 holes, 37 holes, 65 hole. According to the different materials used, it is divided into clay checker bricks and high-alumina checker bricks.
| Grid diameter mm | Seven holes
Fizarana 43 |
Nineteen holes
Φ33 |
Nineteen holes
Φ30 |
Nineteen holes
Φ28 |
Thirty-seven holes
Φ23 |
Thirty-seven holes
Φ20 |
| Unit heating surface m2/m2 | 38.05 | 44.36 | 48.61 | 50.71 | 59.83 | 64.0 |
| Living area m2/m2 | 0.409 | 0.366 | 0.365 | 0.355 | 0.344 | 0.320 |
| Heat storage volume m2/m2 | 0.591 | 0.634 | 0.635 | 0.645 | 0.656 | 0.680 |
| Equivalent thickness mm | 31.07 | 28.60 | 26.14 | 25.44 | 21.93 | 21.25 |
C. Features:
It has a plurality of transparent grid holes parallel to the side surfaces, and positioning protrusions and positioning grooves on the two parallel surfaces.
Good volume stability, excellent high temperature load creep performance, high density and low porosity. Modern blast furnace hot blast stoves usually adopt checkered brick regenerator structure. Perforated checker bricks increase the heating area, reduce the consumption of checker bricks, and greatly reduce the consumption of refractory materials for hot blast stoves, thereby reducing the investment of hot blast stoves.
D. Application:
Currently, checker bricks are mainly used in blast furnace hot blast stoves and flame stoves. Checker bricks are mainly used in the regenerator of hot blast stoves. Checker bricks with lattice holes are arranged in an orderly manner. The upper and lower through holes of the checker bricks can allow gas to pass through. According to the technical requirements of different temperature areas, siliceous checker bricks, clay bricks, etc. are generally used. In some hot blast stoves, high alumina bricks, mullite bricks, sillimanite bricks, etc. are also selected.
E. The function of the hot air stove is to heat the cold air sent by the blower to the blast furnace into hot air, and then the hot air is sent to the blast furnace through the hot air pipe for combustion reaction. The blast furnace hot blast stove has a furnace burning period and an air supply period, and the two working periods are alternated periodically. In the furnace burning period, the high-temperature flue gas after combustion passes through the holes of the checker bricks of the hot blast stove to transfer heat to the checker bricks; during the air supply period, the cold air from the blower enters the hot blast stove and is heated by the checker bricks into hot air. It is sent to the blast furnace through the hot air pipe.
F. Physical and chemical indicators:
| tetikasa | Jereo ny |
| SiO2,% | ≥95 |
| Al2O3,% | ≤1 |
| Fe2O3,% | ≤1.5 |
| Refractoriness, ℃ | ≥1710 |
| Apparent porosity,% | ≤23 |
| Bulk density, g/cm3 | ≥1.9 |
| 0.2MPa load softening start temperature, ℃ | ≥1650 |
| Linear change rate of reheating, 1500℃×4h% | ± 0.2 |
| Creep rate,% | ≤0.2 |
| (0.2MPa, 1500℃, 20-50h) | |
| Residual quartz content% | ≤1.0 |
