- 29
- Jul
The top of the molten pool of the induction melting furnace forms a “hump” working principle
- 29
- 七月
- 29
- 七月
熔池頂部 感應熔煉爐 形成“駝峰”工作原理
在感應熔煉爐的冶煉過程中,金屬材料一旦熔化,熔體在電磁力的作用下就會形成有規律的運動。 這種運動從熔池中心開始,向線圈的兩端移動。 由於金屬受到爐底和爐壁的約束,最終運動始終向上,在熔池頂部形成一個“駝峰”。 有的數據用隆起的高度與熔池直徑的比值來表示熔池的攪拌強度。 “駝峰”的外觀如圖 2-9 所示。
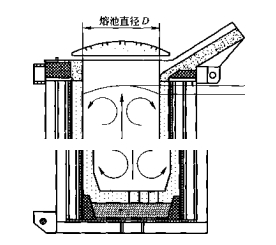
圖2-9 感應熔煉爐熔體“駝峰”形貌示意圖
However, in order to accurately express the shape of the “hump” of the induction melting furnace, and to reveal the flow and deformation behavior of liquid metal under the action of electromagnetic field, it is necessary to solve the Maxwell equations (coupled with Ohm’s law) to obtain the electromagnetic force. The electromagnetic force of is substituted into Navier-Stokes equation and continuity equation as volume force to obtain the flow velocity and free surface shape. At the same time, when the free surface shape of the melt changes, it will inevitably affect the distribution of the electromagnetic field in the melt, and then affect the electromagnetic force acting in the melt, which will change the free surface shape and velocity distribution of the melt. , It can be seen that the flow field and the electromagnetic field are highly coupled.
In order to obtain the morphology of the melt “hump” in the equilibrium state and simplify the calculation process, the following basic assumptions can be made for the induction melting furnace:
(1)由於集膚效應,電流穿透深度3遠小於增加和金屬熔體的尺寸。 因此,作用在熔體中的電磁力可以看成是一種表面力,可以用磁應力張量(磁應力張量)來表示;
(2) The morphological change of the melt “hump” does not affect the distribution of magnetic lines of force in the melt;
(3)如果是裂片銅螺,由於電磁場只能通過裂片之間的縫隙進入熔體,所以電磁場的端部效應很小。 因此,裂片銅內的電磁感應強度增加,是根據無限大螺線管內部的電磁感應強度來計算的。 當系統達到平衡時,駝峰上的表面張力、熔體的靜壓和瞬時平均等效電磁表面力達到平衡。

