- 11
- Feb
Způsob indukčního tepelného zpracování ocelového pásu
Způsob indukčního tepelného zpracování ocelového pásu
Podle požadavků použití musí mít ocelový pás odolnost proti opotřebení a dobrou houževnatost, takže ocelový pás musí být tepelně zpracován, aby se dosáhlo dobrého celkového výkonu. Obrázek 12-59 je schematický diagram zařízení pro indukční tepelné zpracování ocelového pásu. Ocelový pás je ohříván na zhášecí teplotu prvním induktorem a je ochlazován tryskou 7; druhý induktor 8 je temperován a zahříván a poté chlazen vzduchem. Když se ocelový pás ochladí pod 200 °C, tryska 10 rozstřikuje vodu pro rychlé ochlazení na pokojovou teplotu.
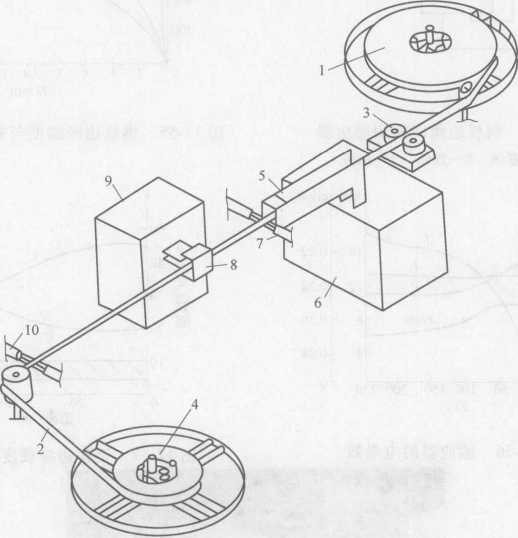
Obrázek 12-59 Zařízení pro indukční tepelné zpracování ocelových pásů
1—Send reel 2-Steel belt 3-Guide wheel 4- Take-up reel 5—Quenching heating inductor
6-Inverter 7—Nozzle 8-Temp heating sensor 9-Inverter 10—Nozzle
U ocelového pásu standardní velikosti používaného jako pásová pila může rychlost jeho pohybu překročit 8 m/min a výkon vysokofrekvenčního generátoru je 10-30 kW.
When the steel strip sent out by the reel has cut serrations, a serrated tip quenching equipment can be placed between the nozzle 10 and the take-up reel 4. The quenching equipment includes an inductor 11 and a quenching nozzle 13 (see Figure 12- 60) The sensor 11 heats the serration tip at a temperature higher than the Curie point, and heats the recessed part between the two teeth at a temperature lower than the Curie point. The hardness of the serration tip can reach 65RC, and it is recessed between two consecutive teeth. The hardness of the part is maintained at the hardness after tempering in the inductor 8.
In some cases, when passing through the sensor 11 and entering the nozzle 13, the steel strip is slightly deformed. In order to avoid this deformation, the sensor 14 is installed on the opposite side of the sensor 11 to be lower than the Curie point. The temperature of the saw blade on the opposite side of the tooth is heated.
Frekvence generátoru dodávaného pro zhášení ohřevu by měla být vyšší než frekvence proudu používaného pro temperovací ohřev.
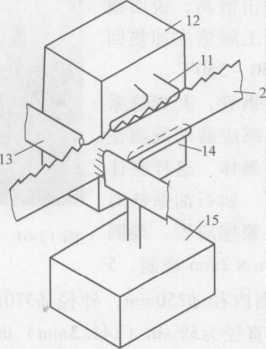
Figure 12-60 Steel band saw tooth induction heating quenching
H—Inductor 12—Inverter 13—Quenching nozzle 14—Inductor 15—Inverter
