- 22
- Aug
Walking induction heating furnace
Walking shigowa dumama tanderu
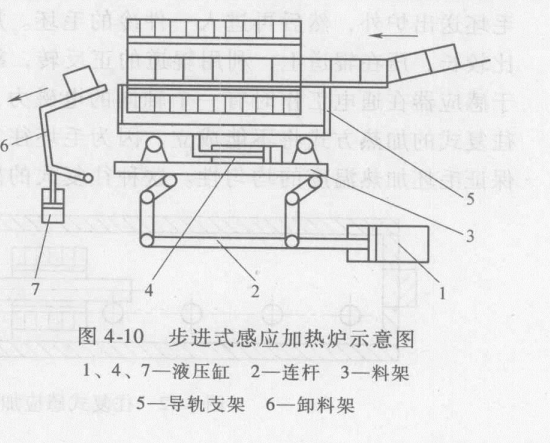
Figure 4-10 is a schematic diagram of a step-by-step induction heating furnace, which is a gradual heating, and the feeding time is determined by the production rate. There are two pairs of independent water-cooled guide rails passing through the coil in the inductor of this kind of stepping induction heating furnace. The blank moves forward at the same time to form a stepping action. That is, when the material needs to be fed, the hydraulic cylinder 1 pulls to the right to lift the material rack 3 through the connecting rod 2, and then the other hydraulic cylinder 4 moves to push the guide rail bracket 5 to move the length of a blank to the left. At this time, the hydraulic cylinder The cylinder 1 is pushed to the left, the material rack 3 is dropped, the blank is placed on the fixed water-cooled guide rail, and the guide rail bracket 5 moves to the right to return to the original position to complete a feeding action. When the blank that has been heated to reach the required temperature is sent to the unloading rack 6, the hydraulic cylinder 7 acts to rotate the unloading rack 6 to make the blank slide down and send it to the next process. Since the blank is lifted and moved, the friction between the blank and the water-cooled guide rail is avoided. However, this step-by-step feeding structure, due to the movable water-cooled guide rail, increases the gap between the blank and the induction coil, and reduces the heating efficiency and power factor of the inductor. And because the movable water-cooled guide rail will lift up all the blanks, the length of the inductor should not be too long, generally not more than Im. For long inductors, it should be designed as several segmented inductors, so that a bracket supporting the movable water-cooled guide rail should be set between the sensors, otherwise the movable water-cooled guide rail may be bent due to the weight of the blank when it is raised. This step-by-step induction heating method is suitable for heating blanks with larger diameters, and is generally used for blanks with a diameter of more than 80mm. Smaller diameter blanks do not need to use this kind of walking induction heating furnace structure, because the structure is more complicated and the cost is relatively high. It is not as convenient and economical as the induction heating furnace with direct feeding method.