- 10
- Oct
How to determine the evaporation temperature and condensation temperature? How to debug?
How to determine the evaporation temperature and condensation temperature? How to debug?
1. Condensing temperature:
The condensation temperature of the compressor system refers to the temperature at which the refrigerant condenses in the condenser, and the refrigerant vapor pressure corresponding to this temperature is the condensation pressure. For water-cooled condensers, the condensing temperature is generally 3-5°C higher than the cooling water temperature.
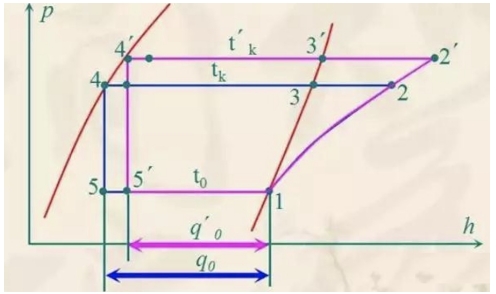
Condensing temperature is one of the main operating parameters in the refrigeration cycle. For the actual refrigeration device, due to the small variation range of other design parameters, the condensation temperature can be said to be the most important operating parameter, which is directly related to the refrigeration effect, safety and reliability of the refrigeration device And energy consumption levels.
2. Evaporation temperature:
Evaporation temperature refers to the temperature at which the refrigerant evaporates and boils in the evaporator. It corresponds to the corresponding evaporation pressure. The evaporation temperature is also an important parameter in the refrigeration system. The evaporation temperature is generally 2-3°C lower than the required water temperature.
The evaporating temperature is the cooling temperature under ideal conditions, but the evaporating temperature of the refrigerant in actual operation is slightly lower than the cooling temperature by 3 to 5 degrees.
3. How to determine the evaporating temperature and condensing temperature in general:
The evaporating temperature and condensing temperature are based on needs, such as air-cooled units. The condensing temperature mainly depends on the ambient temperature, and the evaporating temperature depends on what you apply to. The evaporating temperature of the air conditioner is higher, the cold storage is lower, and the freezing temperature is lower. Even in some low temperature areas, the required evaporation temperature is lower. These parameters are not unified, it mainly depends on the actual application.
You can refer to the following data:
In general, water cooling: evaporating temperature = cold water outlet temperature -5°C (dry evaporator), if it is a flooded evaporator, -2°C. To
Condensing temperature = cooling water outlet temperature + 5°C Air cooling: evaporating temperature = cold water outlet temperature -5~10°C, condensation temperature = ambient temperature + 10~15°C, generally 15. To
4. The influence and adjustment of evaporator temperature on refrigeration:
4.1 The evaporation temperature is equal to the actual outside temperature minus the heat transfer temperature difference. The evaporating temperature is too high, the temperature of the cold air coming out of the evaporator is high, and the temperature is slowed down, or even the expected temperature is not reached at all. The effect on the refrigeration cycle: high superheat, low return pressure, exhaust pressure also decreases, the pressure of the liquid supply pipeline decreases, and the unit flow rate decreases. This cycle causes the warehouse to cool down slowly, the machine keeps working, wears a lot, and the efficiency is low. To
4.2 If the evaporation temperature is too low, there must be a scale. If the head of the machine does not become damp, there is no problem in cooling the warehouse. The exhaust pressure has little effect, and the exhaust temperature decreases. Increased energy consumption. If the evaporating temperature is too low and exceeds the bottom line, there will be liquid in the return air pipe, causing damp trucks, and the consequences will be very serious.
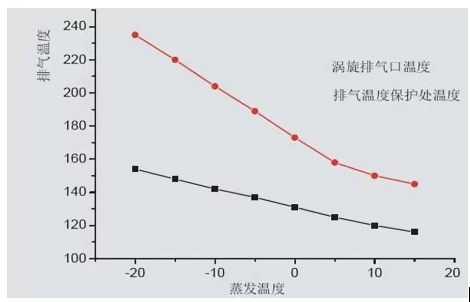 Evaporation temperature adjustment: First of all, we must know that the lower the evaporation pressure, the lower the evaporation temperature. Evaporation temperature adjustment, in actual operation, is to control the evaporation pressure, that is, to adjust the pressure value of the low pressure gauge. During operation, the low pressure pressure is adjusted by adjusting the opening of the thermal expansion valve (or throttle valve). The expansion valve opening degree is large, the evaporation temperature rises, the low pressure pressure also rises, the cooling capacity will increase; if the expansion valve opening degree is small, the evaporation temperature decreases, the low pressure pressure also decreases, and the cooling capacity will decrease.
Evaporation temperature adjustment: First of all, we must know that the lower the evaporation pressure, the lower the evaporation temperature. Evaporation temperature adjustment, in actual operation, is to control the evaporation pressure, that is, to adjust the pressure value of the low pressure gauge. During operation, the low pressure pressure is adjusted by adjusting the opening of the thermal expansion valve (or throttle valve). The expansion valve opening degree is large, the evaporation temperature rises, the low pressure pressure also rises, the cooling capacity will increase; if the expansion valve opening degree is small, the evaporation temperature decreases, the low pressure pressure also decreases, and the cooling capacity will decrease.
