- 02
- Oct
Schematic diagram of various heat exchanger structures
Schematic diagram of various heat exchanger structures
Classified by heat transfer method: heat exchangers can be divided into partition heat exchangers, heat storage heat exchangers, fluid-connected indirect heat exchangers, direct contact heat exchangers, and multiple heat exchangers;
Classified by purpose: it is divided into heater, preheater, superheater, evaporator;
According to the structure, it can be divided into: floating head heat exchanger, fixed tube sheet heat exchanger, U-shaped tube sheet heat exchanger, plate heat exchanger and so on.
1. Floating head heat exchanger
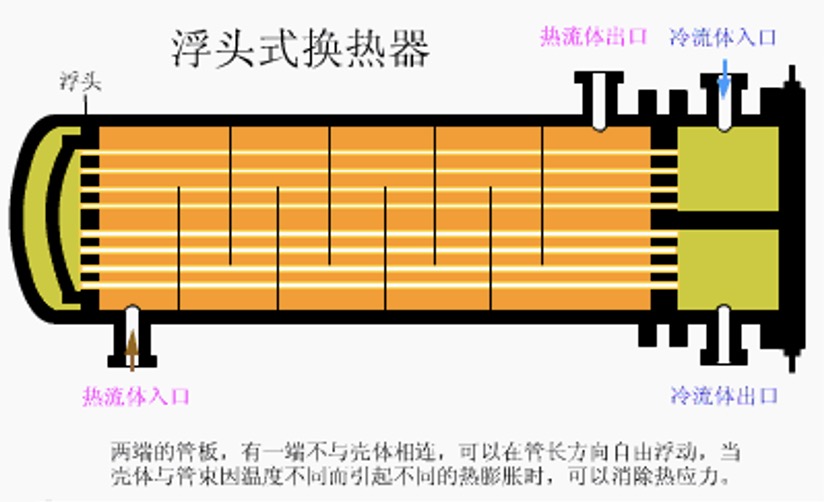
Advantages: Eliminates temperature difference stress, can work under high temperature and high pressure, generally the temperature is less than or equal to 450 degrees, the pressure is less than or equal to 6.4 MPa; the heat exchanger tube bundle can be extracted for cleaning, and can be used in occasions that are prone to scaling or where the tube is prone to corrosion .
Disadvantages: The structure is complex, and the small floating head is prone to internal leakage. The consumption of metal materials is large, and the cost is about 20% higher than that of ordinary heat exchangers.
2. Tubular heat exchanger
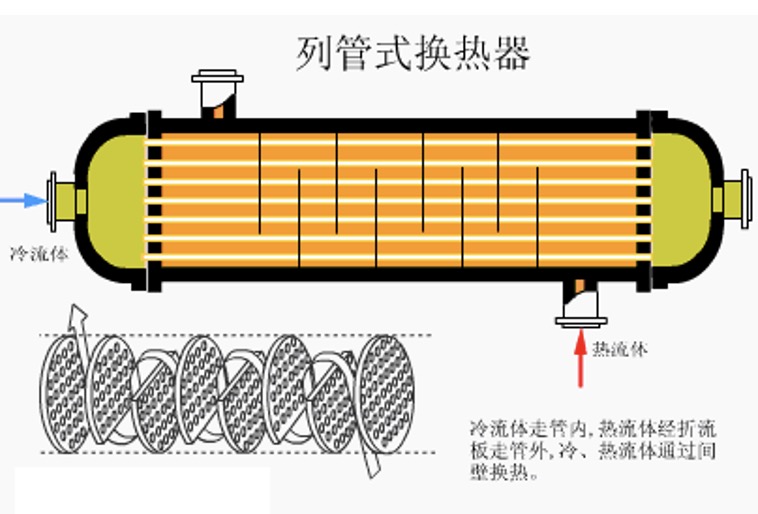
Advantages: simple and compact structure, low cost;
Disadvantages: The outside of the tube cannot be cleaned mechanically, and there is a large temperature difference between the tube wall and the shell wall;
3. U-tube heat exchanger
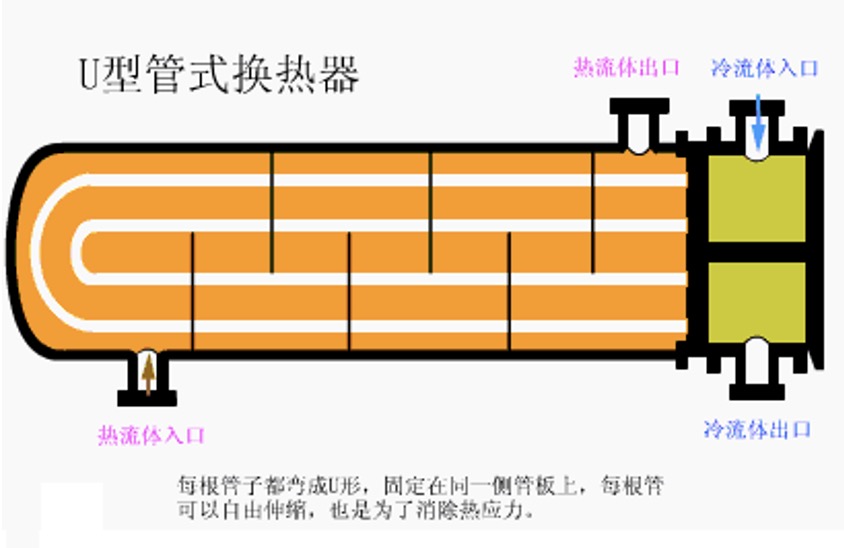
Advantages: the tube bundle can be expanded and contracted freely, there is no thermal stress between the tube and the shell, the tube pass is a double tube pass, the process is long, the heat exchange effect is good, and the pressure bearing capacity is strong; the tube bundle can be drawn out of the shell, which is convenient for maintenance and cleaning, and has a simple structure and low cost;
Disadvantages: inconvenient cleaning in the tube, difficult to replace the tubes in the middle of the tube bundle, the distribution of the tubes is not compact enough, the shell side fluid is easy to short circuit and affect the shell side heat transfer, and the tube will bend and thin, so the straight tube part needs a thicker tube, which limits it The heat exchanger is only suitable for the occasions where the temperature difference between the tube and the shell side is large, or the shell side medium is easy to scale and the tube side medium is clean, high temperature, high pressure, and strong corrosiveness;
4. Immersion coil heat exchanger
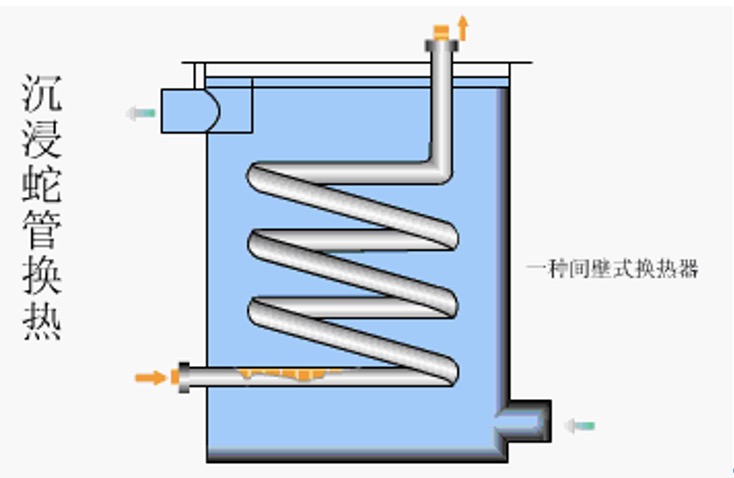
With the serpentine tube as the heat transfer element, according to the different cooling methods of the fluid outside the tube, the serpentine heat exchanger is divided into immersion type and spray type.
Advantages: simple structure, convenient manufacturing, installation, cleaning, inspection and maintenance, convenient for corrosion protection, high pressure bearing, low cost, especially suitable for high-pressure fluid cooling and condensation.
Disadvantages: the equipment is bulky, the consumables are large, and the unit heat transfer requires more metal;
5. Casing type heat exchanger
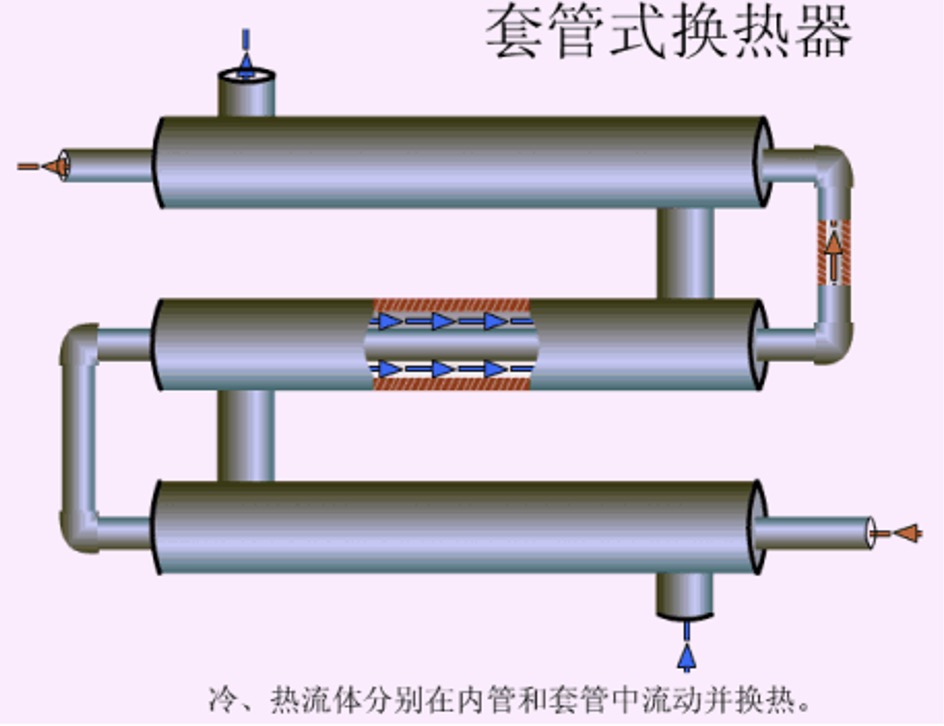
Advantages: large heat exchange area and high heat transfer efficiency;
Disadvantages: troublesome maintenance, cleaning and disassembly, and it is easy to cause leakage at the detachable connection;
6. Spiral plate heat exchanger
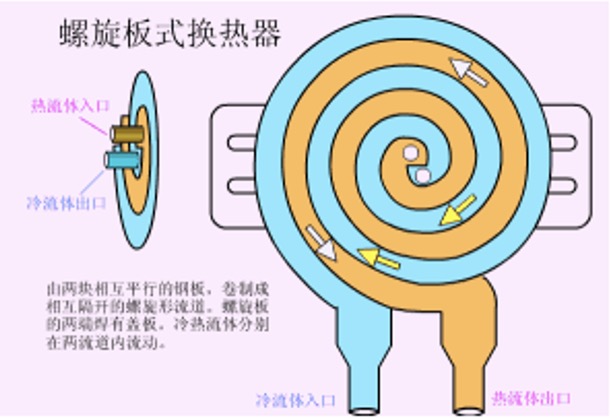
Advantages: good heat transfer efficiency, stable operation, multiple units can be used, high heat transfer efficiency, strong operation reliability, low resistance, etc.;
Disadvantages: high requirements for welding quality, difficult maintenance, heavy weight, poor rigidity, and difficult transportation and installation;
7. Heat exchanger with compensation ring
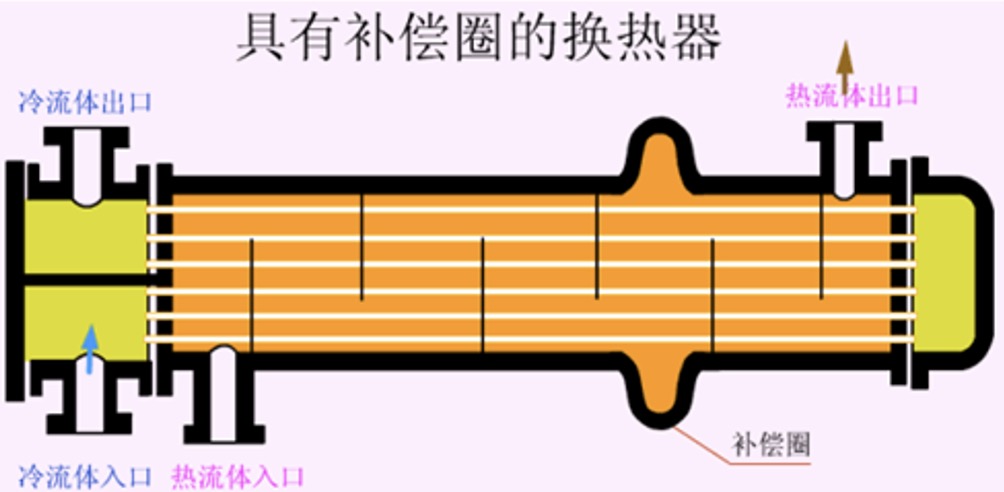
When the fluid is high-temperature heat exchange, the thermal stress on the tube and shell side is relatively large, and the reinforcing ring (or expansion joint) can eliminate the thermal stress. The different thermal expansion degree of the tube, it is suitable for the occasion where the temperature difference between the two fluids is not more than 70℃ and the pressure of the shell side fluid is not more than 600kPa.
8. Heat pipe heat exchanger
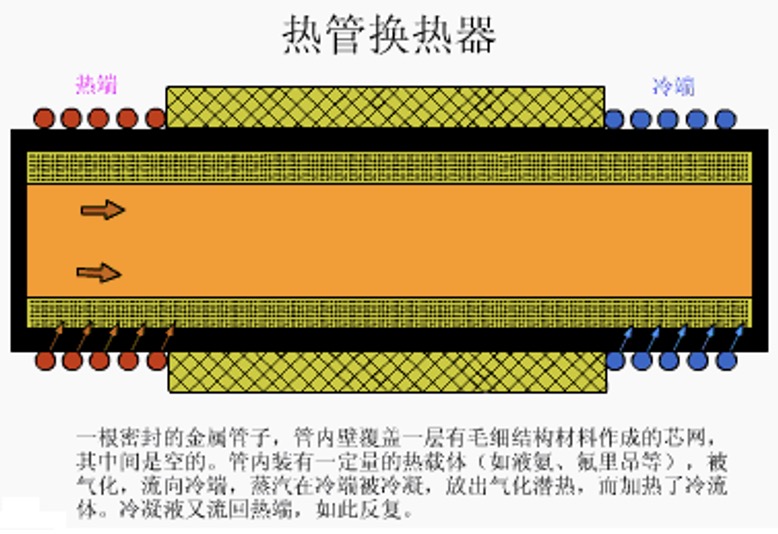
Features: High heat transfer efficiency, compact structure, small resistance loss of heat exchange fluid, flexible shape change, corrosion resistance, and strong environmental adaptability.
9. Jacketed heat exchanger
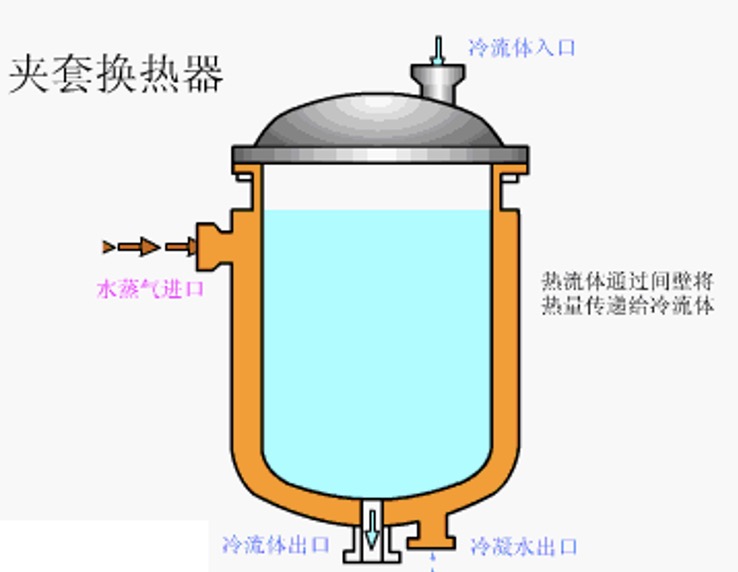
Advantages: simple structure, convenient manufacturing and transportation;
Disadvantages: The heat transfer area is limited, and the heat transfer coefficient is not high. A stirrer or coil can be added to increase the heat transfer coefficient;
10. Plate-fin heat exchanger
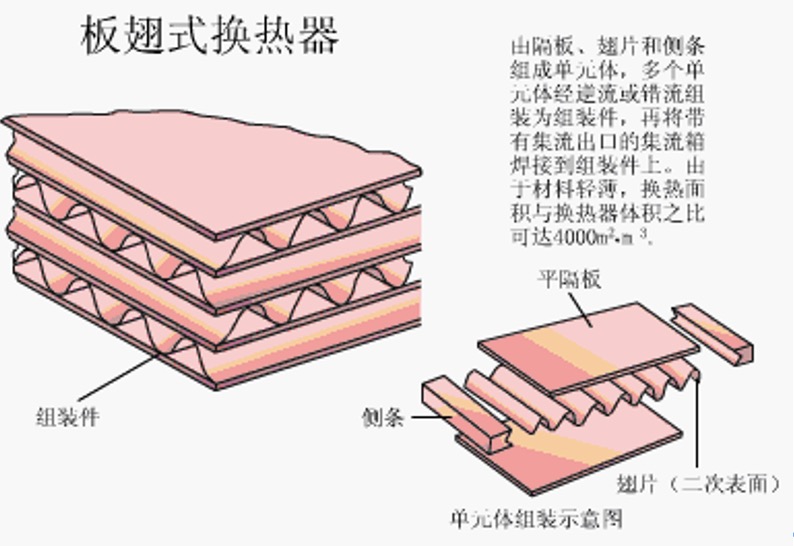
Advantages: compact and lightweight structure, high heat transfer coefficient, strong applicability;
Disadvantages: high manufacturing requirements, complicated process, easy to be blocked, not resistant to corrosion, difficult to inspect and repair, so it is only suitable for cleaning liquids;
Schematic diagram of various heat exchanger structures
Classified by heat transfer method: heat exchangers can be divided into partition heat exchangers, heat storage heat exchangers, fluid-connected indirect heat exchangers, direct contact heat exchangers, and multiple heat exchangers;
Classified by purpose: it is divided into heater, preheater, superheater, evaporator;
According to the structure, it can be divided into: floating head heat exchanger, fixed tube sheet heat exchanger, U-shaped tube sheet heat exchanger, plate heat exchanger and so on.
1. Floating head heat exchanger
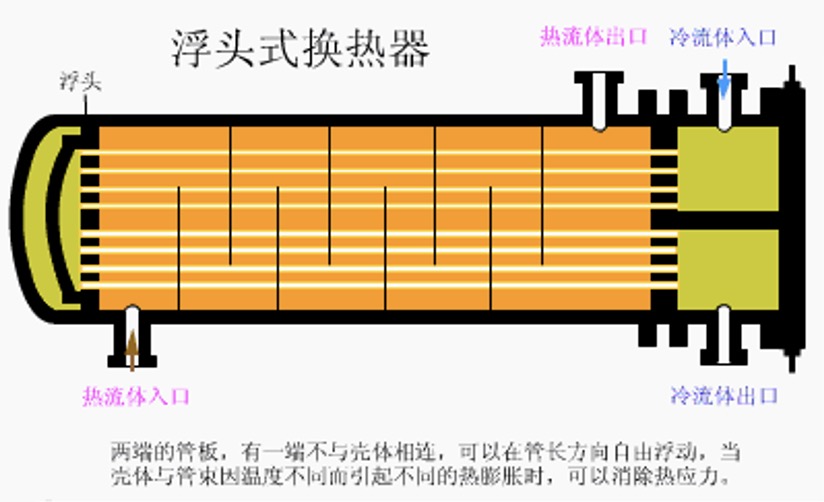
Advantages: Eliminates temperature difference stress, can work under high temperature and high pressure, generally the temperature is less than or equal to 450 degrees, the pressure is less than or equal to 6.4 MPa; the heat exchanger tube bundle can be extracted for cleaning, and can be used in occasions that are prone to scaling or where the tube is prone to corrosion .
Disadvantages: The structure is complex, and the small floating head is prone to internal leakage. The consumption of metal materials is large, and the cost is about 20% higher than that of ordinary heat exchangers.
2. Tubular heat exchanger
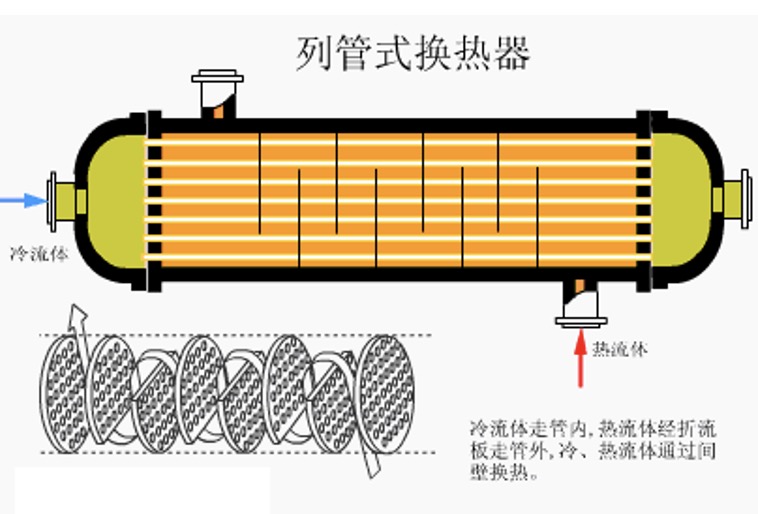
Advantages: simple and compact structure, low cost;
Disadvantages: The outside of the tube cannot be cleaned mechanically, and there is a large temperature difference between the tube wall and the shell wall;
3. U-tube heat exchanger
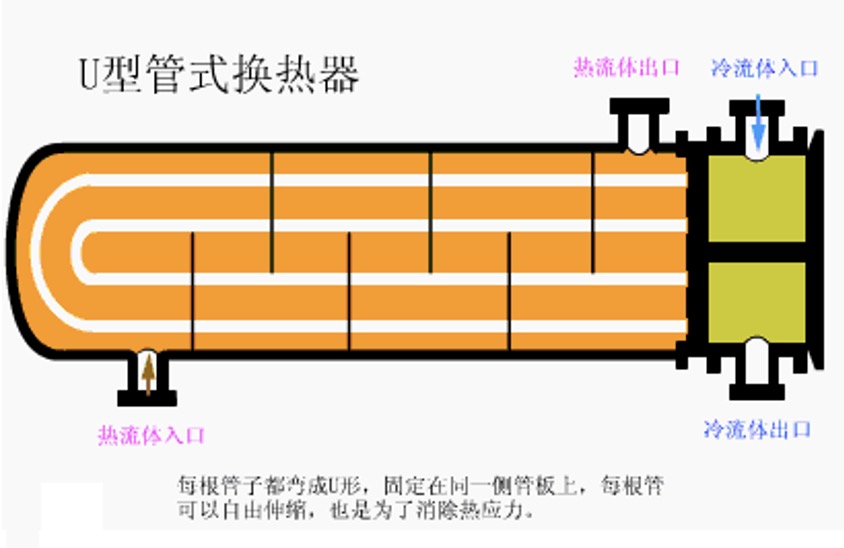
Advantages: the tube bundle can be expanded and contracted freely, there is no thermal stress between the tube and the shell, the tube pass is a double tube pass, the process is long, the heat exchange effect is good, and the pressure bearing capacity is strong; the tube bundle can be drawn out of the shell, which is convenient for maintenance and cleaning, and has a simple structure and low cost;
Disadvantages: inconvenient cleaning in the tube, difficult to replace the tubes in the middle of the tube bundle, the distribution of the tubes is not compact enough, the shell side fluid is easy to short circuit and affect the shell side heat transfer, and the tube will bend and thin, so the straight tube part needs a thicker tube, which limits it The heat exchanger is only suitable for the occasions where the temperature difference between the tube and the shell side is large, or the shell side medium is easy to scale and the tube side medium is clean, high temperature, high pressure, and strong corrosiveness;
4. Immersion coil heat exchanger
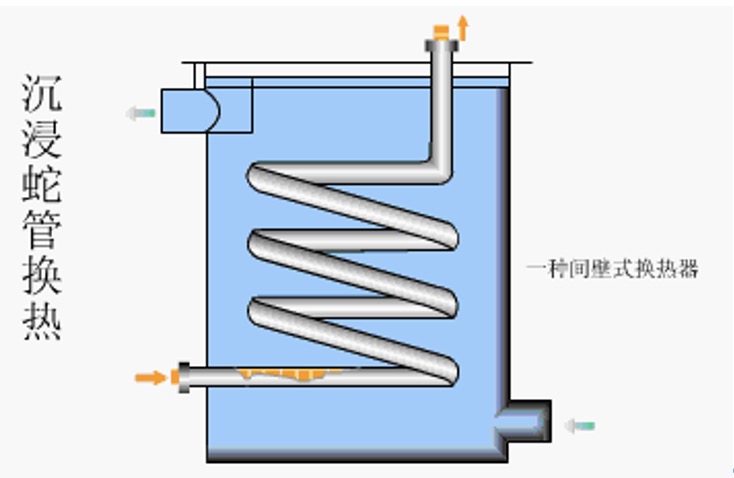
With the serpentine tube as the heat transfer element, according to the different cooling methods of the fluid outside the tube, the serpentine heat exchanger is divided into immersion type and spray type.
Advantages: simple structure, convenient manufacturing, installation, cleaning, inspection and maintenance, convenient for corrosion protection, high pressure bearing, low cost, especially suitable for high-pressure fluid cooling and condensation.
Disadvantages: the equipment is bulky, the consumables are large, and the unit heat transfer requires more metal;
5. Casing type heat exchanger
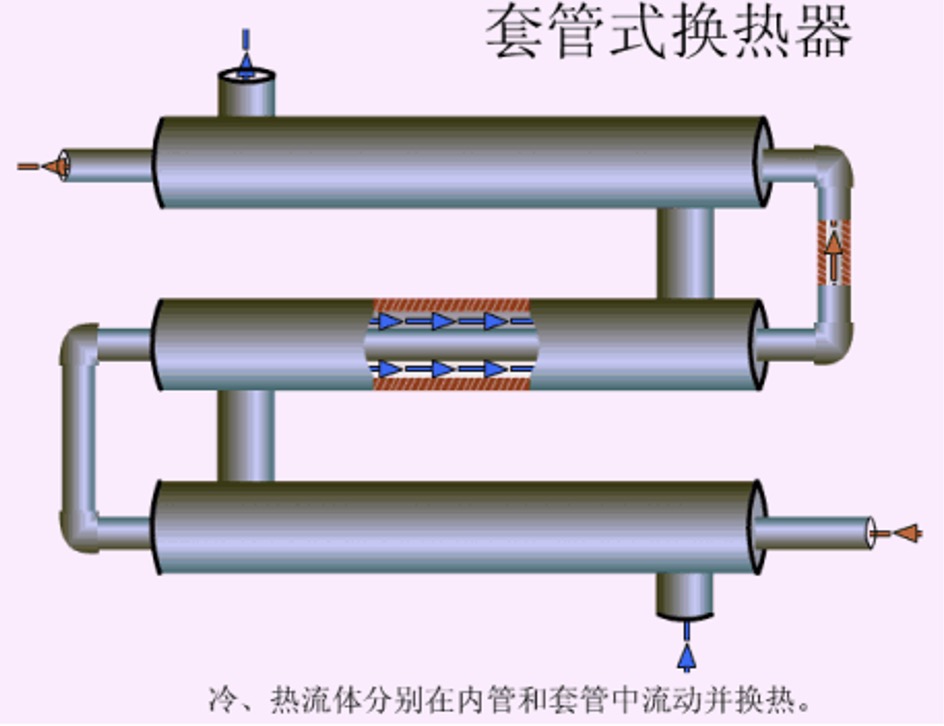
Advantages: large heat exchange area and high heat transfer efficiency;
Disadvantages: troublesome maintenance, cleaning and disassembly, and it is easy to cause leakage at the detachable connection;
6. Spiral plate heat exchanger
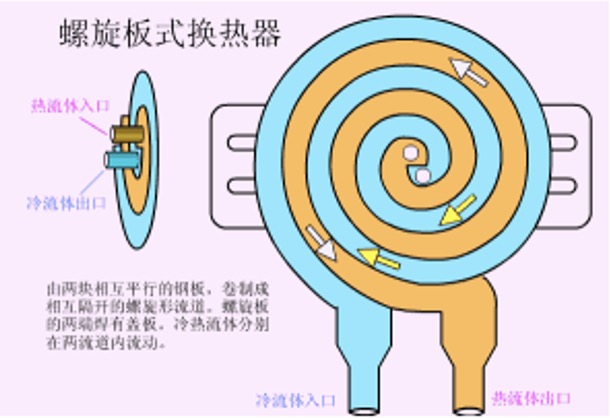
Advantages: good heat transfer efficiency, stable operation, multiple units can be used, high heat transfer efficiency, strong operation reliability, low resistance, etc.;
Disadvantages: high requirements for welding quality, difficult maintenance, heavy weight, poor rigidity, and difficult transportation and installation;
7. Heat exchanger with compensation ring
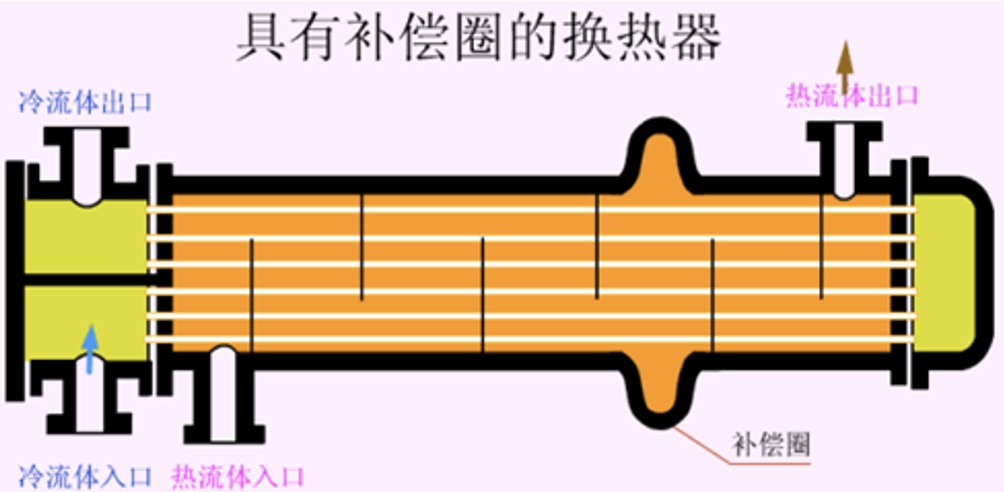
When the fluid is high-temperature heat exchange, the thermal stress on the tube and shell side is relatively large, and the reinforcing ring (or expansion joint) can eliminate the thermal stress. The different thermal expansion degree of the tube, it is suitable for the occasion where the temperature difference between the two fluids is not more than 70℃ and the pressure of the shell side fluid is not more than 600kPa.
8. Heat pipe heat exchanger
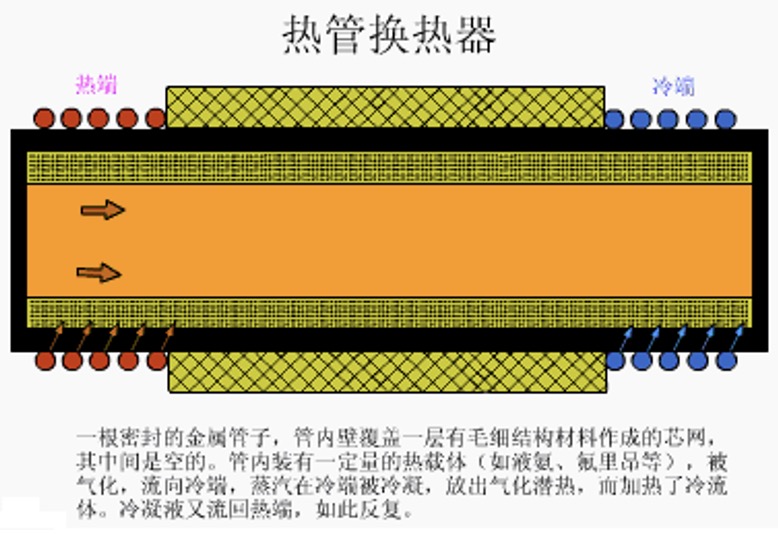
Features: High heat transfer efficiency, compact structure, small resistance loss of heat exchange fluid, flexible shape change, corrosion resistance, and strong environmental adaptability.
9. Jacketed heat exchanger
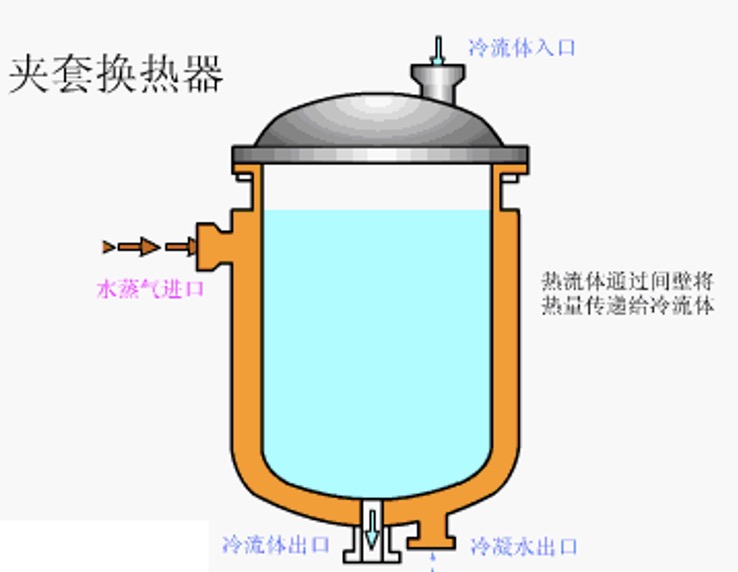
Advantages: simple structure, convenient manufacturing and transportation;
Disadvantages: The heat transfer area is limited, and the heat transfer coefficient is not high. A stirrer or coil can be added to increase the heat transfer coefficient;
10. Plate-fin heat exchanger
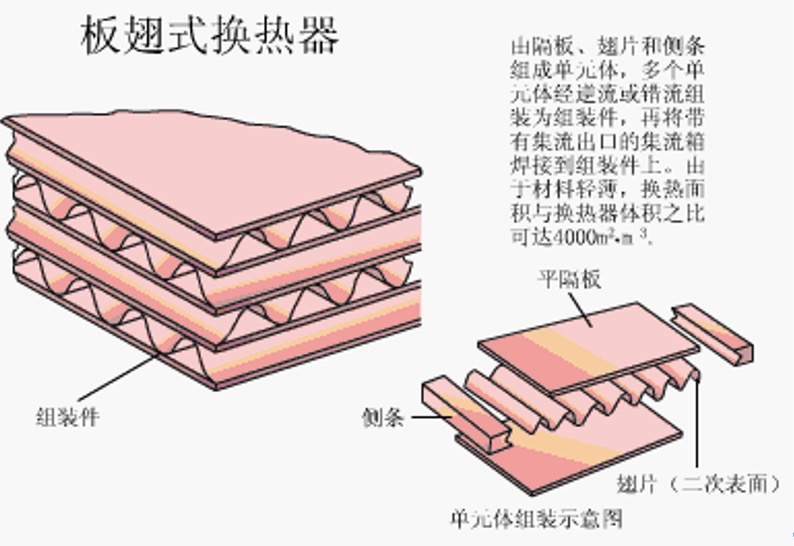
Advantages: compact and lightweight structure, high heat transfer coefficient, strong applicability;
Disadvantages: high manufacturing requirements, complicated process, easy to be blocked, not resistant to corrosion, difficult to inspect and repair, so it is only suitable for cleaning liquids;
