- 16
- Sep
Na-aga n’ihu nkedo tundish a wụrụ awụ ígwè induction akụrụngwa kpo oku
Continuous casting tundish molten steel akụrụngwa ọkụ kpo oku
Nyochaa 1
Tundish molten steel induction heating equipment technology is developed with the progress of continuous casting technology, the improvement of steel quality requirements, the need for energy saving and consumption reduction, and the matching of external refining and continuous casting processes. Different steel grades have different requirements on the AT of molten steel superheat. For thick plates, in order to reduce internal cracks and loose center, the AT should be low (5~200T); for cold-rolled thin plates, the surface is required to have good quality. Higher (15~300℃). However, the molten steel superheat must be stabilized within a certain range to minimize fluctuations. This is a necessary condition to ensure the smooth progress of continuous casting production, prevent nozzle blockage or prevent leaking accidents, and ensure the quality of cast slabs. The enhancement of the heating function of the tundish makes it possible to control the superheat of molten steel stably. The temperature of the molten steel of different ladle fluctuates, which has an adverse effect on the continuous casting process, and the heating of the tundish can compensate for it to some extent. However, it must be pointed out that maintaining a stable molten steel superheat mainly depends on the proper tapping temperature and the adjustment structure after tapping, and the tundish heating can only play a supplementary role. Nevertheless, the heating and control of molten steel in the tundish is still receiving attention from the metallurgical community. Some countries represented by Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and France have successively carried out research on tundish molten steel heating technology from the 1970s to the 1980s. Japan’s Kawasaki Company first developed and obtained a Japanese patent as early as 1982. At present, the tundish molten steel heating technology successfully developed or under development usually adopts the physical heating method. In the physical heating method, electric energy is used as the heat source and converted according to the electric energy. Different mechanisms can be divided into: electromagnetic induction heating equipment, plasma heating, electroslag heating and DC ceramic heating technology.
Ngwa kpo oku induction Tundish nwere njirimara ndị a:
(1) Ọsọ ọkụ ọkụ ngwa ngwa na arụmọrụ ọkụ eletrik dị elu;
(2) Ụfọdụ ụdị nwekwara ụfọdụ electromagnetic ịkpali mmetụta, nke na-eme ka mwepụ nke inclusions;
(3) Usoro okpomọkụ usoro dị mfe ịchịkwa, na ihe kasị mkpa bụ n’ụzọ ziri ezi ịchịkwa superheat nke a wụrụ awụ ígwè;
(4) Ike kpo oku na-ejedebe site na omimi nke ọkwa mmiri mmiri tundish. Naanị mgbe nchara a wụrụ awụ na tundish na-akwakọba n’otu omimi, ikpo ọkụ nwere ike ịga n’ihu nke ọma.
Enwere ọtụtụ ụdị nke tundish induction akụrụngwa kpo oku:
(1) Dị ka ụdị inductor si dị, enwere ike kewaa ya na akụrụngwa ikpo ọkụ induction induction na cored induction kpo oku;
(2) Dị ka ihe owuwu nke inductor si dị, ọ nwere ike kewaa n’ime ụba ụdị mmejọ na ọwara ụdị (groove, wụrụ awụ trenchi) induction kpo oku akụrụngwa;
(3) Dị ka akụkụ kpo oku si dị, enwere ike kewaa ya na kpo oku mpaghara na ikpo ọkụ n’ozuzu ya.
2 Na-aga n’ihu nkedo tundish a wụrụ awụ igwe elektrọn magnetik induction ngwaọrụ kpo oku
2. 1 Tundish electromagnetic induction akụrụngwa kpo oku dakọtara na kehoraizin na-aga n’ihu nkedo igwe
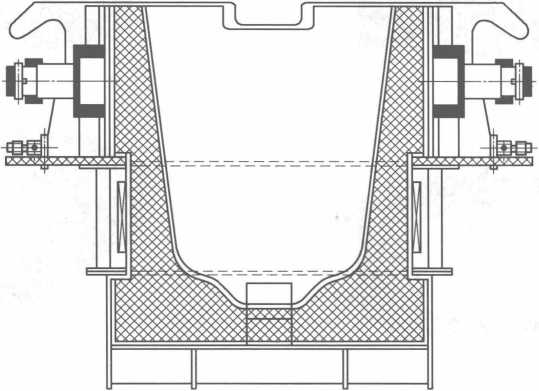
Akụrụngwa ọkụ induction tundish electromagnetic dabara na igwe nkedo kwụ ọtọ na-aga n’ihu ka egosiri na eserese 10-7.
A na-akọwa usoro mmepụta nke igwe anaghị agba nchara.
Ọgụgụ 10-7 Tundish electromagnetic induction akụrụngwa kpo oku dabara na igwe nkedo na-aga n’ihu na kwụ ọtọ
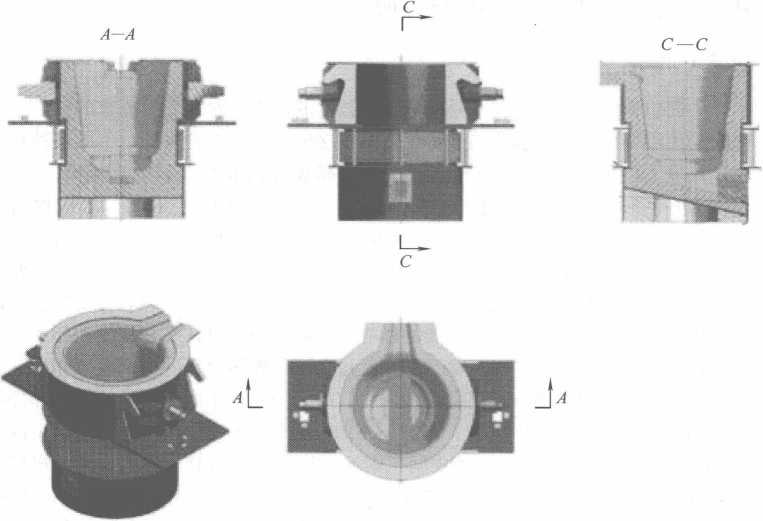
 Ka agbachara ụdị igwe anaghị agba nchara niile, a na-ebunye ha n’ime ọkụ induction atọ 5t site na tank nri nwere cranes. Mgbe agbazechara nchara ahụ ka ọ bụrụ okpomọkụ achọrọ (ihe dị ka 1650 Celsius), a na-awụsa nchara a wụrụ awụ n’ime ọkụ induction n’ime ladle, wee jiri gwongworo ahụ na-awụsa nchara a wụrụ awụ n’ime ọkụ 8t AOD, ebe ọ na-enweta decarburization. slagging, dephosphorization na sulfur mwepụ, na nhazi nke ihe mejupụtara alloy (karịsịa Cr, Ni), na mgbe ahụ, nchara a wụrụ awụ (ihe mejupụtara na okpomọkụ na-emezu ihe ndị a chọrọ) Tinye nchara a wụrụ awụ na ladle n’ime ladle ma jiri kreenu wụsa. igwe a wụrụ awụ na ladle n’ime oghere nke 8t electromagnetic induction akụrụngwa kpo oku. A na-adọta mmiri mmiri igwe anaghị agba nchara na-ekpo ọkụ site na nchekwa ọkụ wee tụba ya n’ogwe okirikiri site na igwe nkedo na-aga n’ihu na-aga n’ihu wee tinye ya n’ihe ndina jụrụ oyi site n’ịkpụ na ịkpụ. .
Ka agbachara ụdị igwe anaghị agba nchara niile, a na-ebunye ha n’ime ọkụ induction atọ 5t site na tank nri nwere cranes. Mgbe agbazechara nchara ahụ ka ọ bụrụ okpomọkụ achọrọ (ihe dị ka 1650 Celsius), a na-awụsa nchara a wụrụ awụ n’ime ọkụ induction n’ime ladle, wee jiri gwongworo ahụ na-awụsa nchara a wụrụ awụ n’ime ọkụ 8t AOD, ebe ọ na-enweta decarburization. slagging, dephosphorization na sulfur mwepụ, na nhazi nke ihe mejupụtara alloy (karịsịa Cr, Ni), na mgbe ahụ, nchara a wụrụ awụ (ihe mejupụtara na okpomọkụ na-emezu ihe ndị a chọrọ) Tinye nchara a wụrụ awụ na ladle n’ime ladle ma jiri kreenu wụsa. igwe a wụrụ awụ na ladle n’ime oghere nke 8t electromagnetic induction akụrụngwa kpo oku. A na-adọta mmiri mmiri igwe anaghị agba nchara na-ekpo ọkụ site na nchekwa ọkụ wee tụba ya n’ogwe okirikiri site na igwe nkedo na-aga n’ihu na-aga n’ihu wee tinye ya n’ihe ndina jụrụ oyi site n’ịkpụ na ịkpụ. .
Ihe anụ ahụ nke 8t electromagnetic induction kpo oku ladle ka egosiri na eserese 10-8.
8t na 14t tundish electromagnetic induction kpo oku akụrụngwa, tundish induction kpo oku akụrụngwa nwere ike ịchịkwa okpomọkụ nke nchara a wụrụ awụ (njọ njehie bụ naanị ± 5 ~ 6 ℃), si otú a na-ahụ na ịdịmma nke billet. Na mgbakwunye, oge mgbanwe okpomọkụ nke tundish nwekwara ike ịgbatị n’ụzọ kwesịrị ekwesị, na-egosi mmetụta dị mma nke induction ngwa kpo oku.
2. 2 Ngwa Tundish nke induction kpo oku akụrụngwa nke arc na-aga n’ihu nkedo igwe
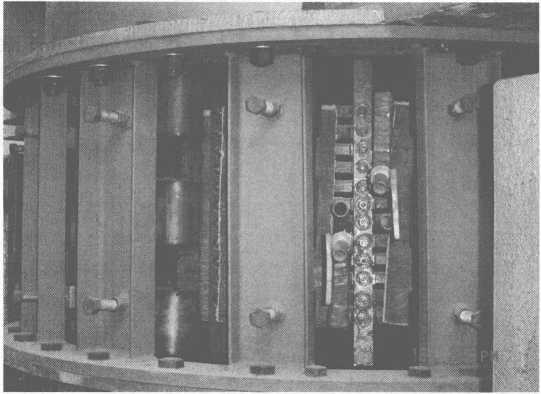
Ngwa tundish nke akụrụngwa kpo oku induction nke igwe nkedo arc na-aga n’ihu ka egosiri na eserese 10-9.
Mgbe arc billet na-aga n’ihu na-anakwere ngwa ọkụ ọkụ ọkụ ọkụ ọkụ tundish, enwere ike ibelata okpomọkụ nke ịkụ ọkpọ (dịka ọmụmaatụ, ọ nwere ike ịbụ.
Ọgụgụ 10-9 Ngwa Tundish nke induction akụrụngwa kpo oku nke arc na-aga n’ihu nkedo igwe
Site na 1700 ° C ruo 1650 Celsius C), nke a abụghị naanị na-enyere aka melite ndụ nke mkpuchi ọkụ nchara (onye ntụgharị, ọkụ ọkụ eletrik ma ọ bụ ọkụ induction), kamakwa na-eme ka ọnọdụ okpomọkụ nke igwe gbazere sie ike na nkedo na-aga n’ihu ma na-ekwe nkwa ịdị mma nke na-aga n’ihu. nkedo mpempe akwụkwọ.
Dabere na okwu mmeghe a dị n’elu, enwere ike ịtụle na ihe nkedo na-aga n’ihu na tundish magnetik induction akụrụngwa kpo oku bụ teknụzụ na-echekwa ume ọhụrụ na gburugburu ebe obibi. Nkwenye nke ngwaọrụ a bụ ọrụ mgbanwe teknụzụ dịtụ mma maka ụlọ ọrụ igwe, ọ tozurukwa nkwalite na iji ya.
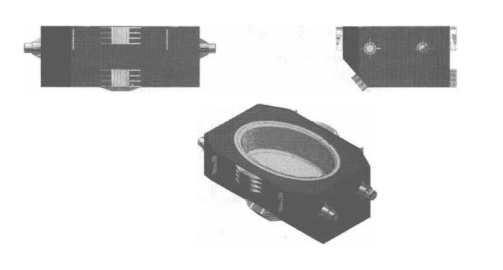
Ọgụgụ 10-10 na-egosi 16t tundish electromagnetic induction akụrụngwa kpo oku.
Ọgụgụ 10-10 16t tundish electromagnetic induction akụrụngwa kpo oku
Onyonyo 10-11 bụ schematic eserese nke tundish nke 14t induction akụrụngwa kpo oku.
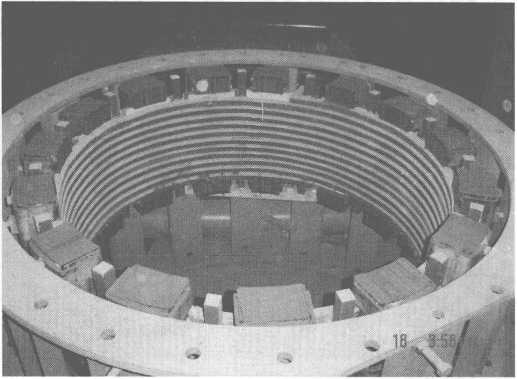
Ọgụgụ 10-11 Eserese atụmatụ nke tundish nke 14t induction akụrụngwa kpo oku