- 23
- May
Padayon nga paghulma sa tundish nga tinunaw nga steel induction heating equipment
Padayon nga paghulma sa tundish nga tinunaw nga steel induction heating equipment
1 Sumaryo
Tundish molten steel induction heating equipment technology is developed with the progress of continuous casting technology, the improvement of steel quality requirements, the need for energy saving and consumption reduction, and the matching of external refining and continuous casting processes. Different steel grades have different requirements on the AT of molten steel superheat. For thick plates, in order to reduce internal cracks and loose center, the AT should be low (5~200T); for cold-rolled thin plates, the surface is required to have good quality. Higher (15~300℃). However, the molten steel superheat must be stabilized within a certain range to minimize fluctuations. This is a necessary condition to ensure the smooth progress of continuous casting production, prevent nozzle blockage or prevent leaking accidents, and ensure the quality of cast slabs. The enhancement of the heating function of the tundish makes it possible to control the superheat of molten steel stably. The temperature of the molten steel of different ladle fluctuates, which has an adverse effect on the continuous casting process, and the heating of the tundish can compensate for it to some extent. However, it must be pointed out that maintaining a stable molten steel superheat mainly depends on the proper tapping temperature and the adjustment structure after tapping, and the tundish heating can only play a supplementary role. Nevertheless, the heating and control of molten steel in the tundish is still receiving attention from the metallurgical community. Some countries represented by Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and France have successively carried out research on tundish molten steel heating technology from the 1970s to the 1980s. Japan’s Kawasaki Company first developed and obtained a Japanese patent as early as 1982. At present, the tundish molten steel heating technology successfully developed or under development usually adopts the physical heating method. In the physical heating method, electric energy is used as the heat source and converted according to the electric energy. Different mechanisms can be divided into: electromagnetic induction heating equipment, plasma heating, electroslag heating and DC ceramic heating technology.
Ang Tundish induction heating equipment adunay mga mosunod nga mga kinaiya:
(1) Katulin sa pagpainit ug taas nga kahusayan sa pagpainit sa kuryente;
(2) Ang ubang mga matang usab adunay usa ka piho nga electromagnetic stirring effect, nga makatabang sa pagtangtang sa mga inklusyon;
(3) Ang temperatura sa proseso dali nga makontrol, ug ang labing hinungdanon nga butang mao ang mas tukma nga pagkontrol sa sobrang kainit sa tinunaw nga asero;
(4) Ang gahum sa pagpainit limitado sa giladmon sa tundish liquid level. Lamang sa diha nga ang tinunaw nga asero sa tundish natapok sa usa ka piho nga giladmon, ang pagpainit mahimong magpadayon nga hapsay.
Adunay daghang mga lahi sa tundish induction heating equipment:
(1) Sumala sa matang sa inductor, kini mahimong bahinon ngadto sa coreless induction heating equipment ug cored induction heating equipment;
(2) Sumala sa gambalay sa inductor, kini mahimong bahinon ngadto sa dugang nga sayop nga matang ug tunnel matang (groove, tinunaw kanal) induction pagpainit ekipo;
(3) Sumala sa bahin sa pagpainit, kini mahimong bahinon ngadto sa lokal nga pagpainit ug kinatibuk-ang pagpainit.
2 Padayon nga paghulma sa tundish nga tinunaw nga asero nga electromagnetic induction heating equipment device
2. 1 Tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment nga gipares sa pinahigda nga padayon nga casting machine
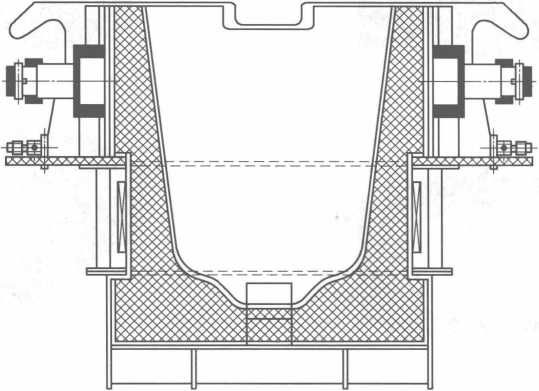
Ang tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment nga gipares sa pinahigda nga padayon nga casting machine gipakita sa Figure 10-7.
Ang proseso sa produksiyon sa usa ka planta nga stainless steel gipatin-aw na karon.

Figure 10-7 Tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment nga gipares sa pinahigda nga padayon nga casting machine
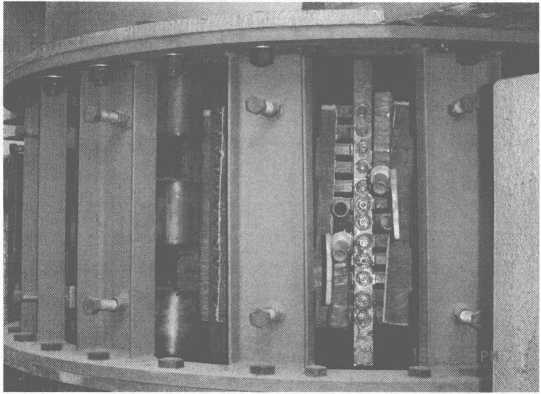 Pagkahuman sa tanan nga mga matang sa stainless steel nga batched, kini gikarga sa tulo ka 5t induction furnaces gikan sa feeding tank nga adunay mga crane. Human matunaw ang scrap steel sa gikinahanglan nga temperatura (mga 1650 ° C), ang tinunaw nga asero sa induction furnace gibubo ngadto sa ladle, ug dayon gigamit Ang trak nagbubo sa tinunaw nga puthaw ngadto sa 8t AOD furnace, diin kini moagi sa decarburization, slagging, dephosphorization ug sulfur pagtangtang, ug pag-adjust sa komposisyon sa haluang metal (nag-una Cr, Ni), ug unya ang tinunaw nga asero (ang komposisyon ug temperatura sa pagsugat sa mga kinahanglanon) Ibutang ang tinunaw nga puthaw sa ladle ngadto sa ladle ug sa paggamit sa crane sa pagbubo ang tinunaw nga asero sa ladle ngadto sa ladle sa 8t electromagnetic induction heating equipment. Ang stainless steel nga likido nga gipainit pinaagi sa pagpreserbar sa kainit gikuha ug gihulog sa usa ka lingin nga bar pinaagi sa usa ka pinahigda nga padayon nga makina sa paghulma ug sa katapusan giduso ngadto sa makapabugnaw nga higdaanan pinaagi sa pagporma ug paggunting. .
Pagkahuman sa tanan nga mga matang sa stainless steel nga batched, kini gikarga sa tulo ka 5t induction furnaces gikan sa feeding tank nga adunay mga crane. Human matunaw ang scrap steel sa gikinahanglan nga temperatura (mga 1650 ° C), ang tinunaw nga asero sa induction furnace gibubo ngadto sa ladle, ug dayon gigamit Ang trak nagbubo sa tinunaw nga puthaw ngadto sa 8t AOD furnace, diin kini moagi sa decarburization, slagging, dephosphorization ug sulfur pagtangtang, ug pag-adjust sa komposisyon sa haluang metal (nag-una Cr, Ni), ug unya ang tinunaw nga asero (ang komposisyon ug temperatura sa pagsugat sa mga kinahanglanon) Ibutang ang tinunaw nga puthaw sa ladle ngadto sa ladle ug sa paggamit sa crane sa pagbubo ang tinunaw nga asero sa ladle ngadto sa ladle sa 8t electromagnetic induction heating equipment. Ang stainless steel nga likido nga gipainit pinaagi sa pagpreserbar sa kainit gikuha ug gihulog sa usa ka lingin nga bar pinaagi sa usa ka pinahigda nga padayon nga makina sa paghulma ug sa katapusan giduso ngadto sa makapabugnaw nga higdaanan pinaagi sa pagporma ug paggunting. .
Ang pisikal nga butang sa 8t electromagnetic induction heating equipment ladle gipakita sa Figure 10-8.
Ang 8t ug 14t tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment, ang tundish induction heating equipment mahimong estrikto ug tukma nga makontrol ang temperatura sa tinunaw nga asero (ang error range mao lamang ± 5 ~ 6 ℃), sa ingon masiguro ang kalidad sa billet. Dugang pa, ang oras sa pag-adjust sa temperatura sa tundish mahimo usab nga tukma nga mapalawig, nga nagpakita sa maayong epekto sa kagamitan sa pagpainit sa induction.
2. 2 Tundish device sa induction heating equipment sa arc padayon nga casting machine
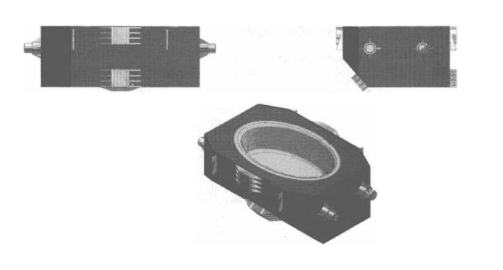
Ang tundish device sa induction heating equipment sa arc continuous casting machine gipakita sa Figure 10-9.
Human ang arc billet padayon nga caster mosagop sa electromagnetic induction heating equipment tundish, ang tapping temperature mahimong ipaubos (pananglitan, mahimo kini
Figure 10-9 Tundish device sa induction heating equipment sa arc padayon nga casting machine
Gikan sa 1700 ° C ngadto sa 1650 ° C), kini dili lamang makatabang sa pagpalambo sa kinabuhi sa steelmaking furnace lining (converter, electric arc furnace o induction furnace), apan nagpalig-on usab sa temperatura sa tinunaw nga asero sa padayon nga paghulma ug naggarantiya sa kalidad sa padayon nga paghulma sa mga billet.
Pinasukad sa pasiuna sa itaas, mahimong makonsiderar nga ang padayon nga paghulma sa tundish magnetic induction heating equipment usa ka bag-ong teknolohiya nga makaluwas sa enerhiya ug mahigalaon sa kalikopan. Ang pagsagop sa kini nga aparato usa ka medyo sulundon nga proyekto sa pagbag-o sa teknolohiya alang sa mga negosyo nga metalurhiko, ug kini takus sa promosyon ug paggamit.
Ang Figure 10-10 nagpakita sa 16t tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment.
Figure 10-10 16t tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment
Ang Figure 10-11 usa ka schematic diagram sa tundish sa 14t induction heating equipment.
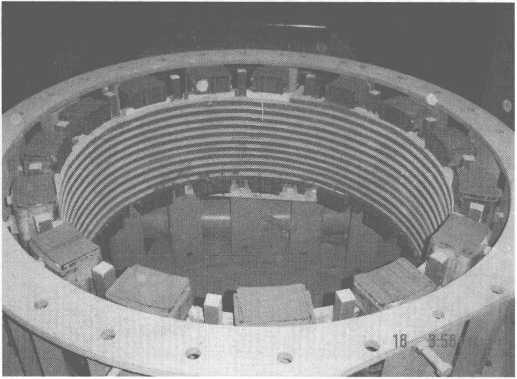
Figure 10-11 Schematic diagram sa tundish sa 14t induction heating equipment