- 23
- May
Nruam casting tundish molten steel induction cua sov khoom
Nruam casting tundish molten steel induction cua sov khoom
1 Txheej txheem cej luam
Tundish molten steel induction cua sov khoom technology is developed with the progress of continuous casting technology, the improvement of steel quality requirements, the need for energy saving and consumption reduction, and the matching of external refining and continuous casting processes. Different steel grades have different requirements on the AT of molten steel superheat. For thick plates, in order to reduce internal cracks and loose center, the AT should be low (5~200T); for cold-rolled thin plates, the surface is required to have good quality. Higher (15~300℃). However, the molten steel superheat must be stabilized within a certain range to minimize fluctuations. This is a necessary condition to ensure the smooth progress of continuous casting production, prevent nozzle blockage or prevent leaking accidents, and ensure the quality of cast slabs. The enhancement of the heating function of the tundish makes it possible to control the superheat of molten steel stably. The temperature of the molten steel of different ladle fluctuates, which has an adverse effect on the continuous casting process, and the heating of the tundish can compensate for it to some extent. However, it must be pointed out that maintaining a stable molten steel superheat mainly depends on the proper tapping temperature and the adjustment structure after tapping, and the tundish heating can only play a supplementary role. Nevertheless, the heating and control of molten steel in the tundish is still receiving attention from the metallurgical community. Some countries represented by Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and France have successively carried out research on tundish molten steel heating technology from the 1970s to the 1980s. Japan’s Kawasaki Company first developed and obtained a Japanese patent as early as 1982. At present, the tundish molten steel heating technology successfully developed or under development usually adopts the physical heating method. In the physical heating method, electric energy is used as the heat source and converted according to the electric energy. Different mechanisms can be divided into: electromagnetic induction heating equipment, plasma heating, electroslag heating and DC ceramic heating technology.
Tundish induction cua sov cov cuab yeej muaj cov yam ntxwv hauv qab no:
(1) Cov cua kub ceev ceev thiab hluav taws xob hluav taws xob ua haujlwm siab;
(2) Qee hom kuj muaj qee yam electromagnetic stirring effect, uas yog qhov tsim nyog rau kev tshem tawm cov kev suav nrog;
(3) Cov txheej txheem kub yog ib qho yooj yim los tswj, thiab qhov tseem ceeb tshaj plaws yog kom tswj tau qhov superheat ntawm cov hlau molten;
(4) Lub zog cua sov yog txwv los ntawm qhov tob ntawm tundish kua theem. Tsuas yog thaum cov hlau molten nyob rau hauv lub tundish accumulates mus rau ib tug tej yam qhov tob, lub cua sov yuav mus smoothly.
Muaj ntau ntau hom tundish induction cua sov khoom siv:
(1) Raws li hom inductor, nws tuaj yeem muab faib ua coreless induction cua sov khoom thiab cored induction cua sov khoom;
(2) Raws li cov qauv ntawm cov inductor, nws tuaj yeem muab faib ua ntau hom kev ua txhaum thiab hom qhov (groove, molten trench) induction cua sov khoom;
(3) Raws li qhov cua sov, nws tuaj yeem muab faib ua cov cua sov hauv zos thiab tag nrho cov cua sov.
2 Nruam casting tundish molten steel electromagnetic induction cua sov khoom siv
2. 1 Tundish electromagnetic induction cua sov khoom siv nrog kab rov tav nruam casting tshuab
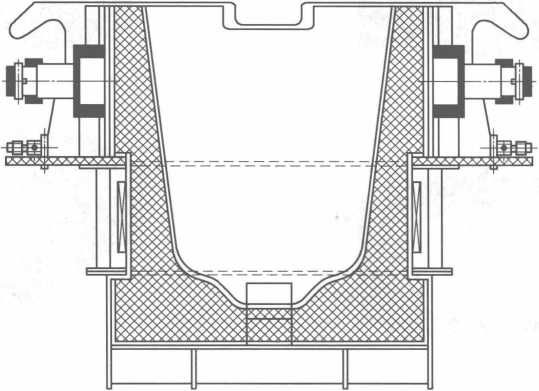
Lub tundish electromagnetic induction cua sov cov cuab yeej txuam nrog kab rov tav nruam casting tshuab yog qhia nyob rau hauv daim duab 10-7.
Kev tsim cov txheej txheem ntawm cov nroj tsuag stainless hlau yog tam sim no piav qhia.

Daim duab 10-7 Tundish electromagnetic induction cua sov khoom siv nrog kab rov tav nruam casting tshuab
 Tom qab txhua yam ntawm stainless hlau yog batched, lawv tau loaded rau hauv peb 5t induction furnaces los ntawm lub tank pub nrog cranes. Tom qab cov seem hlau yog melted mus rau qhov yuav tsum tau kub (kwv yees li 1650 ° C), cov hlau molten nyob rau hauv lub induction rauv yog poured rau hauv lub ladle, thiab ces siv lub tsheb pours lub molten steel rau hauv lub 8t AOD rauv, qhov twg nws undergoes decarburization, slagging, dephosphorization thiab sulfur tshem tawm, thiab kho cov alloy muaj pes tsawg leeg (feem ntau yog Cr, Ni), thiab ces molten steel (qhov muaj pes tsawg leeg thiab kub raws li qhov yuav tsum tau) Muab cov hlau molten nyob rau hauv lub ladle rau hauv lub ladle thiab siv lub crane los ncuav. molten hlau nyob rau hauv lub ladle rau hauv lub ladle ntawm 8t electromagnetic induction cua sov khoom. Cov kua stainless hlau rhuab los ntawm kev txuag hluav taws xob yog kos thiab muab pov rau hauv ib puag ncig bar los ntawm kab rov tav nruam casting tshuab thiab thaum kawg thawb mus rau hauv lub txaj txias los ntawm kev sib sau thiab shearing. .
Tom qab txhua yam ntawm stainless hlau yog batched, lawv tau loaded rau hauv peb 5t induction furnaces los ntawm lub tank pub nrog cranes. Tom qab cov seem hlau yog melted mus rau qhov yuav tsum tau kub (kwv yees li 1650 ° C), cov hlau molten nyob rau hauv lub induction rauv yog poured rau hauv lub ladle, thiab ces siv lub tsheb pours lub molten steel rau hauv lub 8t AOD rauv, qhov twg nws undergoes decarburization, slagging, dephosphorization thiab sulfur tshem tawm, thiab kho cov alloy muaj pes tsawg leeg (feem ntau yog Cr, Ni), thiab ces molten steel (qhov muaj pes tsawg leeg thiab kub raws li qhov yuav tsum tau) Muab cov hlau molten nyob rau hauv lub ladle rau hauv lub ladle thiab siv lub crane los ncuav. molten hlau nyob rau hauv lub ladle rau hauv lub ladle ntawm 8t electromagnetic induction cua sov khoom. Cov kua stainless hlau rhuab los ntawm kev txuag hluav taws xob yog kos thiab muab pov rau hauv ib puag ncig bar los ntawm kab rov tav nruam casting tshuab thiab thaum kawg thawb mus rau hauv lub txaj txias los ntawm kev sib sau thiab shearing. .
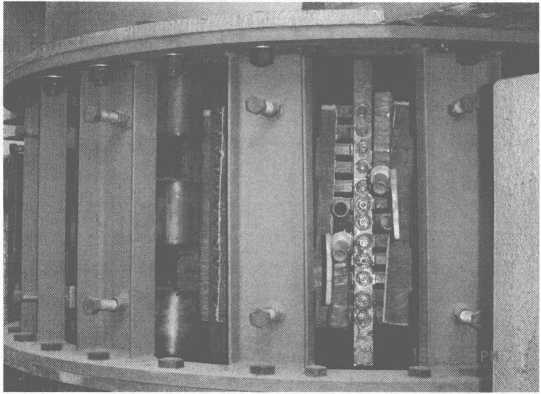
Lub cev khoom ntawm 8t electromagnetic induction cua sov ladle yog qhia hauv daim duab 10-8.
8t thiab 14t tundish electromagnetic induction cua sov cov cuab yeej, tundish induction cua sov cov cuab yeej tuaj yeem tswj tau qhov kub thiab txias ntawm cov hlau molten (qhov kev ua yuam kev tsuas yog ± 5 ~ 6 ℃), yog li ua kom cov khoom zoo ntawm cov hlau. Tsis tas li ntawd, lub sijhawm hloov kho qhov kub thiab txias ntawm tundish kuj tuaj yeem tsim nyog txuas ntxiv, uas qhia txog cov txiaj ntsig zoo ntawm cov khoom siv cua sov induction.
2. 2 Tundish ntaus ntawv ntawm induction cua sov khoom ntawm arc nruam casting tshuab
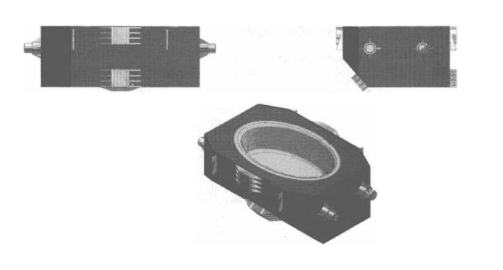
Cov cuab yeej tundish ntawm cov khoom siv cua sov induction ntawm lub tshuab arc nruam casting yog qhia hauv daim duab 10-9.
Tom qab lub arc billet nruam caster txais cov khoom siv hluav taws xob induction cua sov tundish, tapping kub tuaj yeem txo qis (piv txwv li, nws tuaj yeem ua tau.
Daim duab 10-9 Tundish ntaus ntawv ntawm induction cua sov khoom ntawm arc nruam casting tshuab
Los ntawm 1700 ° C mus rau 1650 ° C), qhov no tsis tsuas yog pab txhim kho lub neej ntawm steelmaking rauv hauv ob sab phlu (converter, hluav taws xob arc rauv los yog induction rauv), tab sis kuj stabilizes kub ntawm molten hlau nyob rau hauv nruam casting thiab guarantees qhov zoo ntawm nruam. casting billets.
Raws li cov lus qhia saum toj no, nws tuaj yeem txiav txim siab tias qhov nruam nruam casting tundish magnetic induction cua sov cov cuab yeej yog lub zog txuag hluav taws xob tshiab thiab ib puag ncig-phooj ywg. Kev saws me nyuam ntawm cov cuab yeej no yog ib qho kev hloov kho thev naus laus zis zoo tshaj plaws rau kev lag luam metallurgical, thiab nws tsim nyog rau kev nce qib thiab siv.
Daim duab 10-10 qhia txog 16t tundish electromagnetic induction cua sov khoom.
Daim duab 10-10 16t tundish electromagnetic induction cua sov khoom
Daim duab 10-11 yog daim duab schematic ntawm tundish ntawm 14t induction cua sov khoom.
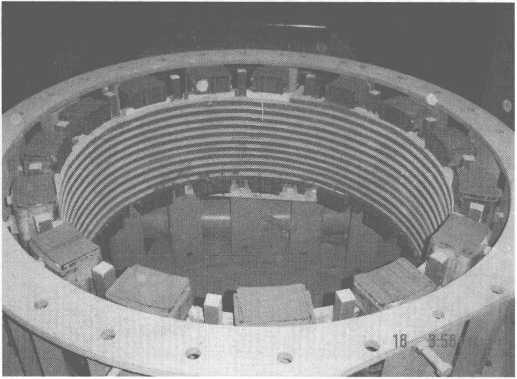
Daim duab 10-11 Schematic daim duab ntawm tundish ntawm 14t induction cua sov khoom