- 23
- May
連鑄中間包鋼水感應加熱設備
連鑄中間包鋼水感應加熱設備
1概述
Tundish molten steel 感應加熱設備 technology is developed with the progress of continuous casting technology, the improvement of steel quality requirements, the need for energy saving and consumption reduction, and the matching of external refining and continuous casting processes. Different steel grades have different requirements on the AT of molten steel superheat. For thick plates, in order to reduce internal cracks and loose center, the AT should be low (5~200T); for cold-rolled thin plates, the surface is required to have good quality. Higher (15~300℃). However, the molten steel superheat must be stabilized within a certain range to minimize fluctuations. This is a necessary condition to ensure the smooth progress of continuous casting production, prevent nozzle blockage or prevent leaking accidents, and ensure the quality of cast slabs. The enhancement of the heating function of the tundish makes it possible to control the superheat of molten steel stably. The temperature of the molten steel of different ladle fluctuates, which has an adverse effect on the continuous casting process, and the heating of the tundish can compensate for it to some extent. However, it must be pointed out that maintaining a stable molten steel superheat mainly depends on the proper tapping temperature and the adjustment structure after tapping, and the tundish heating can only play a supplementary role. Nevertheless, the heating and control of molten steel in the tundish is still receiving attention from the metallurgical community. Some countries represented by Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and France have successively carried out research on tundish molten steel heating technology from the 1970s to the 1980s. Japan’s Kawasaki Company first developed and obtained a Japanese patent as early as 1982. At present, the tundish molten steel heating technology successfully developed or under development usually adopts the physical heating method. In the physical heating method, electric energy is used as the heat source and converted according to the electric energy. Different mechanisms can be divided into: electromagnetic induction heating equipment, plasma heating, electroslag heating and DC ceramic heating technology.
中間包感應加熱設備具有以下特點:
(1)加熱速度快,電加熱效率高;
(2)有的還具有一定的電磁攪拌作用,有利於夾雜物的去除;
(3)工藝溫度易於控制,最重要的是更準確地控製鋼水過熱度;
(4)加熱功率受中間包液面深度的限制。 只有當中間包內的鋼水積聚到一定深度時,加熱才能順利進行。
中間包感應加熱設備有以下幾種類型:
(1)按感應器的種類可分為無芯感應加熱設備和有芯感應加熱設備;
(2)根據感應器的結構,可分為增加故障型和隧道型(槽、熔槽)感應加熱設備;
(3)按加熱部位可分為局部加熱和整體加熱。
2 連鑄中間包鋼水電磁感應加熱設備裝置
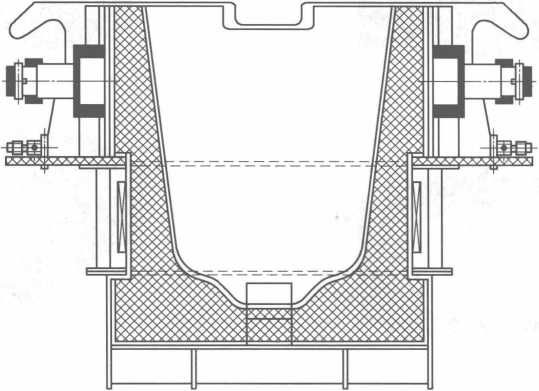
2. 1 與臥式連鑄機配套的中間包電磁感應加熱設備
與臥式連鑄機配套的中間包電磁感應加熱設備如圖10-7所示。
現在說明不銹鋼廠的生產過程。

圖10-7 與臥式連鑄機配套的中間包電磁感應加熱設備
 各種不銹鋼配料後,用起重機從進料槽裝入5台1650t感應爐。 廢鋼熔化至所需溫度(約8°C)後,將感應爐中的鋼水倒入鋼包中,然後用卡車將鋼水倒入8t AOD爐中,在那裡進行脫碳,排渣、脫磷、除硫,調整合金成分(主要是Cr、Ni),然後出鋼水(成分和溫度符合要求)將鋼包內的鋼水倒入XNUMXt電磁感應加熱設備的鋼包中。 經保溫加熱的不銹鋼液經臥式連鑄機拉鑄成圓棒,最後經成型剪切推入冷床。 .
各種不銹鋼配料後,用起重機從進料槽裝入5台1650t感應爐。 廢鋼熔化至所需溫度(約8°C)後,將感應爐中的鋼水倒入鋼包中,然後用卡車將鋼水倒入8t AOD爐中,在那裡進行脫碳,排渣、脫磷、除硫,調整合金成分(主要是Cr、Ni),然後出鋼水(成分和溫度符合要求)將鋼包內的鋼水倒入XNUMXt電磁感應加熱設備的鋼包中。 經保溫加熱的不銹鋼液經臥式連鑄機拉鑄成圓棒,最後經成型剪切推入冷床。 .
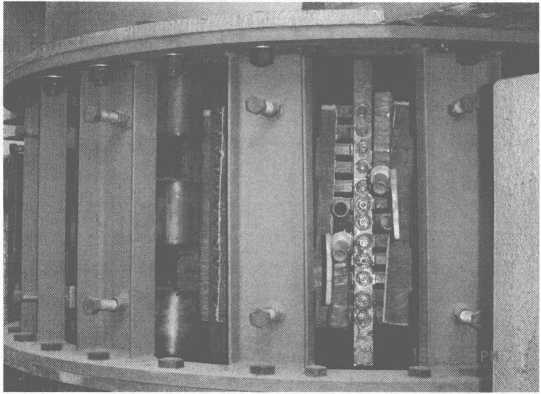
8t電磁感應加熱設備鋼包實物如圖10-8所示。
8t、14t中間包電磁感應加熱設備,中間包感應加熱設備能嚴格準確地控製鋼水溫度(誤差範圍僅為±5~6℃),從而保證鋼坯質量。 此外,中間包的調溫時間也可以適當延長,顯示出感應加熱設備的良好效果。
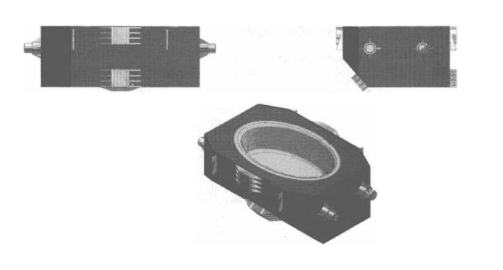
2. 2 電弧連鑄機感應加熱設備中間包裝置
電弧連鑄機感應加熱設備的中間包裝置如圖10-9所示。
弧坯連鑄機採用電磁感應加熱設備中間包後,可降低出鋼溫度(如可
圖10-9 電弧連鑄機感應加熱設備中間包裝置
從 1700°C 到 1650°C),這不僅有助於提高煉鋼爐襯(轉爐、電弧爐或感應爐)的壽命,而且穩定連鑄時鋼水溫度,保證連鑄質量。鑄坯。
綜合以上介紹,可以認為連鑄中間包磁感應加熱設備是一項節能環保的新技術。 採用該裝置是冶金企業比較理想的技改項目,值得推廣使用。
10t中間包電磁感應加熱設備如圖10-16所示。
圖10-10 16t中間包電磁感應加熱設備
圖10-11為14t感應加熱設備中間包示意圖。
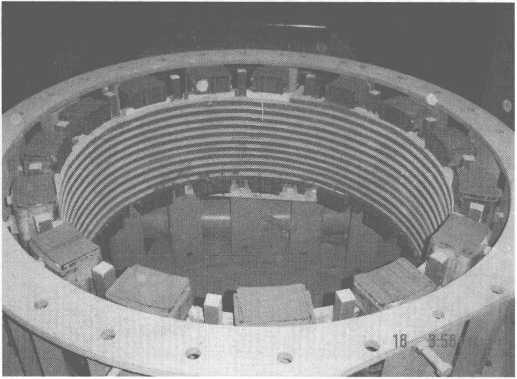
圖10-11 14t感應加熱設備中間包示意圖