- 23
- May
연속주조 턴디쉬 용강유도가열장치
연속주조 턴디쉬 용강유도가열장치
1 개요
Tundish molten steel 유도 가열 장치 technology is developed with the progress of continuous casting technology, the improvement of steel quality requirements, the need for energy saving and consumption reduction, and the matching of external refining and continuous casting processes. Different steel grades have different requirements on the AT of molten steel superheat. For thick plates, in order to reduce internal cracks and loose center, the AT should be low (5~200T); for cold-rolled thin plates, the surface is required to have good quality. Higher (15~300℃). However, the molten steel superheat must be stabilized within a certain range to minimize fluctuations. This is a necessary condition to ensure the smooth progress of continuous casting production, prevent nozzle blockage or prevent leaking accidents, and ensure the quality of cast slabs. The enhancement of the heating function of the tundish makes it possible to control the superheat of molten steel stably. The temperature of the molten steel of different ladle fluctuates, which has an adverse effect on the continuous casting process, and the heating of the tundish can compensate for it to some extent. However, it must be pointed out that maintaining a stable molten steel superheat mainly depends on the proper tapping temperature and the adjustment structure after tapping, and the tundish heating can only play a supplementary role. Nevertheless, the heating and control of molten steel in the tundish is still receiving attention from the metallurgical community. Some countries represented by Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and France have successively carried out research on tundish molten steel heating technology from the 1970s to the 1980s. Japan’s Kawasaki Company first developed and obtained a Japanese patent as early as 1982. At present, the tundish molten steel heating technology successfully developed or under development usually adopts the physical heating method. In the physical heating method, electric energy is used as the heat source and converted according to the electric energy. Different mechanisms can be divided into: electromagnetic induction heating equipment, plasma heating, electroslag heating and DC ceramic heating technology.
Tundish 유도 가열 장비에는 다음과 같은 특성이 있습니다.
(1) 빠른 가열 속도와 높은 전기 가열 효율;
(2) 일부 유형에는 특정 전자기 교반 효과가있어 내포물 제거에 도움이됩니다.
(3) 공정 온도는 제어하기 쉽고 가장 중요한 것은 용강의 과열도를보다 정확하게 제어하는 것입니다.
(4) 화력은 턴디쉬 수위의 깊이에 의해 제한됩니다. 턴디쉬 내부의 용강이 일정 깊이까지 축적되어야만 가열이 원활하게 진행될 수 있습니다.
턴디쉬 유도 가열 장비에는 여러 유형이 있습니다.
(1) 인덕터의 유형에 따라 코어리스 유도 가열 장비와 코어형 유도 가열 장비로 나눌 수 있습니다.
(2) 인덕터의 구조에 따라 증가 결함 유형과 터널 유형 (그루브, 용융 트렌치) 유도 가열 장치로 나눌 수 있습니다.
(3) 난방 부분에 따라 국부 난방과 전체 난방으로 나눌 수 있습니다.
2 연속주조 턴디쉬 용강 전자유도 가열장치 장치
2. 수평 연속 주조기와 일치하는 1 Tundish 전자기 유도 가열 장비
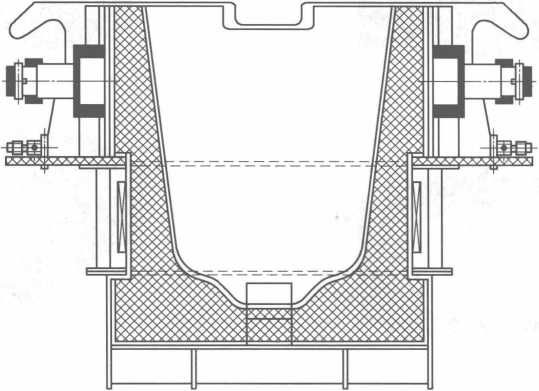
수평 연속 주조기와 일치하는 턴디쉬 전자기 유도 가열 장비는 그림 10-7에 나와 있습니다.
이제 스테인리스 스틸 공장의 생산 공정에 대해 설명합니다.

그림 10-7 수평연속주조기와 결합된 턴디쉬 전자기유도가열장치
 모든 종류의 스테인리스 스틸이 배치된 후 크레인이 있는 공급 탱크에서 5개의 1650t 유도로에 로드됩니다. 고철이 필요한 온도(약 8°C)로 녹은 후 유도로의 용강을 국자에 붓고 사용합니다. 트럭이 용강을 8t AOD로에 부어 탈탄, 슬래깅, 탈인 및 황 제거 및 합금 조성(주로 Cr, Ni) 조정 후 용강(조성 및 온도가 요구 사항 충족) 국자에 용강을 넣고 크레인을 사용하여 붓는다. XNUMXt 전자기 유도 가열 장비의 국자로 국자의 용강. 보온에 의해 가열된 스테인리스강 액체를 수평연속주조기에 의해 환봉으로 끌어내어 주조하고, 최종적으로 성형 및 전단에 의해 냉각층으로 밀어넣는다. .
모든 종류의 스테인리스 스틸이 배치된 후 크레인이 있는 공급 탱크에서 5개의 1650t 유도로에 로드됩니다. 고철이 필요한 온도(약 8°C)로 녹은 후 유도로의 용강을 국자에 붓고 사용합니다. 트럭이 용강을 8t AOD로에 부어 탈탄, 슬래깅, 탈인 및 황 제거 및 합금 조성(주로 Cr, Ni) 조정 후 용강(조성 및 온도가 요구 사항 충족) 국자에 용강을 넣고 크레인을 사용하여 붓는다. XNUMXt 전자기 유도 가열 장비의 국자로 국자의 용강. 보온에 의해 가열된 스테인리스강 액체를 수평연속주조기에 의해 환봉으로 끌어내어 주조하고, 최종적으로 성형 및 전단에 의해 냉각층으로 밀어넣는다. .
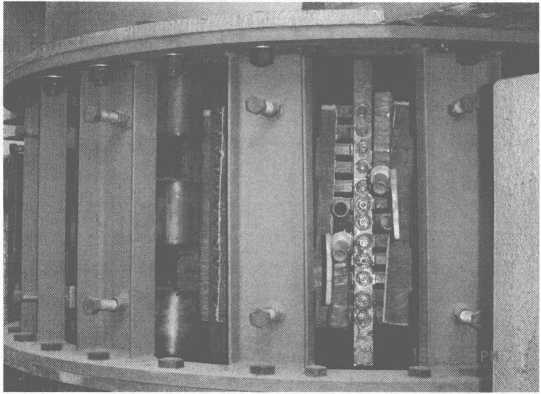
8t 전자기 유도 가열 장비 국자의 물리적 대상은 그림 10-8에 나와 있습니다.
8t 및 14t 턴디쉬 전자기 유도 가열 장비인 턴디쉬 유도 가열 장비는 용강의 온도를 엄격하고 정확하게 제어할 수 있으므로(오차 범위는 ±5~6℃에 불과함) 빌릿의 품질을 보장합니다. 또한, 턴디쉬의 온도 조정 시간도 적절하게 연장될 수 있어 유도 가열 장비의 좋은 효과를 보여줍니다.
2. 2 아크 연속 주조기의 유도 가열 장치의 턴디쉬 장치
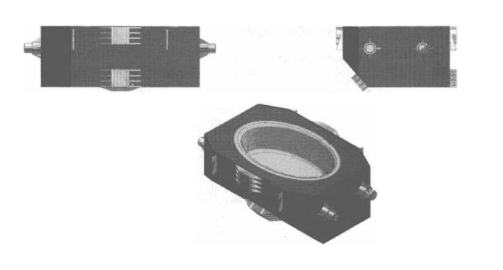
아크 연속 주조기의 유도 가열 장치의 턴디쉬 장치는 그림 10-9에 나와 있습니다.
아크 빌렛 연속 주조기가 전자 유도 가열 장비 턴디쉬를 채택한 후 탭핑 온도를 낮출 수 있습니다 (예를 들어,
그림 10-9 아크 연속 주조기의 유도 가열 장치의 턴디쉬 장치
1700°C ~ 1650°C)에서 제강로 라이닝(컨버터, 전기로 또는 유도로)의 수명을 향상시킬 뿐만 아니라 연속 주조에서 용강의 온도를 안정화하고 연속 주조 품질을 보장합니다. 주조 빌릿.
위의 소개를 바탕으로 연속 주조 턴디쉬 자기 유도 가열 장치는 새로운 에너지 절약 및 환경 친화적 인 기술이라고 생각할 수 있습니다. 이 장치의 채택은 야금 기업을 위한 비교적 이상적인 기술 변환 프로젝트이며 홍보 및 사용 가치가 있습니다.
그림 10-10은 16t 턴디쉬 전자기 유도 가열 장비를 보여줍니다.
그림 10-10 16t 턴디쉬 전자기 유도 가열 장치
그림 10-11은 14t 유도 가열 장비의 턴디쉬 개략도입니다.
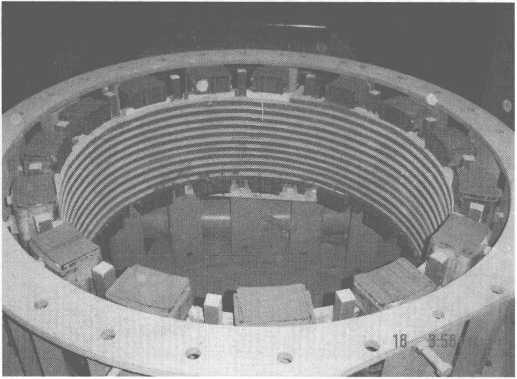
그림 10-11 14t 유도 가열 장치의 턴디쉬 개략도