- 23
- May
連続鋳造タンディッシュ溶鋼誘導加熱装置
連続鋳造タンディッシュ溶鋼誘導加熱装置
1概要
Tundish molten steel 誘導加熱装置 technology is developed with the progress of continuous casting technology, the improvement of steel quality requirements, the need for energy saving and consumption reduction, and the matching of external refining and continuous casting processes. Different steel grades have different requirements on the AT of molten steel superheat. For thick plates, in order to reduce internal cracks and loose center, the AT should be low (5~200T); for cold-rolled thin plates, the surface is required to have good quality. Higher (15~300℃). However, the molten steel superheat must be stabilized within a certain range to minimize fluctuations. This is a necessary condition to ensure the smooth progress of continuous casting production, prevent nozzle blockage or prevent leaking accidents, and ensure the quality of cast slabs. The enhancement of the heating function of the tundish makes it possible to control the superheat of molten steel stably. The temperature of the molten steel of different ladle fluctuates, which has an adverse effect on the continuous casting process, and the heating of the tundish can compensate for it to some extent. However, it must be pointed out that maintaining a stable molten steel superheat mainly depends on the proper tapping temperature and the adjustment structure after tapping, and the tundish heating can only play a supplementary role. Nevertheless, the heating and control of molten steel in the tundish is still receiving attention from the metallurgical community. Some countries represented by Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and France have successively carried out research on tundish molten steel heating technology from the 1970s to the 1980s. Japan’s Kawasaki Company first developed and obtained a Japanese patent as early as 1982. At present, the tundish molten steel heating technology successfully developed or under development usually adopts the physical heating method. In the physical heating method, electric energy is used as the heat source and converted according to the electric energy. Different mechanisms can be divided into: electromagnetic induction heating equipment, plasma heating, electroslag heating and DC ceramic heating technology.
タンディッシュ誘導加熱装置には、次の特徴があります。
(1)速い加熱速度と高い電気加熱効率。
(2)一部のタイプには、特定の電磁攪拌効果もあり、これは介在物の除去に役立ちます。
(3)プロセス温度の制御が容易であり、最も重要なことは、溶鋼の過熱度をより正確に制御することです。
(4)加熱力は、タンディッシュ液面の深さによって制限されます。 タンディッシュの溶鋼が一定の深さまで溜まるとスムーズに加熱できます。
タンディッシュ誘導加熱装置にはいくつかの種類があります。
(1)インダクタの種類に応じて、コアレス誘導加熱装置とコア誘導加熱装置に分けることができます。
(2)インダクタの構造に応じて、増加断層タイプとトンネルタイプ(溝、溶融トレンチ)の誘導加熱装置に分けることができます。
(3)暖房部分によって、局所暖房と全体暖房に分けることができます。
2連続鋳造タンディッシュ溶鋼電磁誘導加熱装置装置
2水平連続鋳造機に適合したタンディッシュ電磁誘導加熱装置
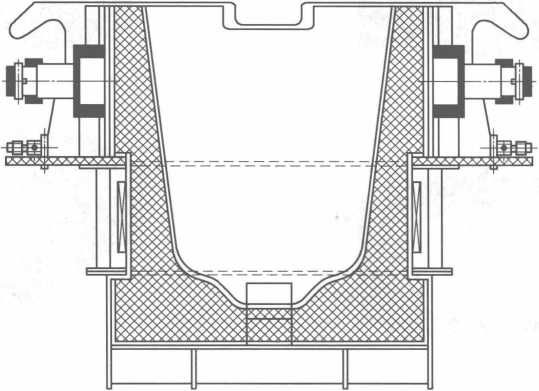
図10-7に、水平連続鋳造機と組み合わせたタンディッシュ電磁誘導加熱装置を示します。
ここでは、ステンレス工場の製造工程について説明します。

図10-7水平連続鋳造機と組み合わせたタンディッシュ電磁誘導加熱装置
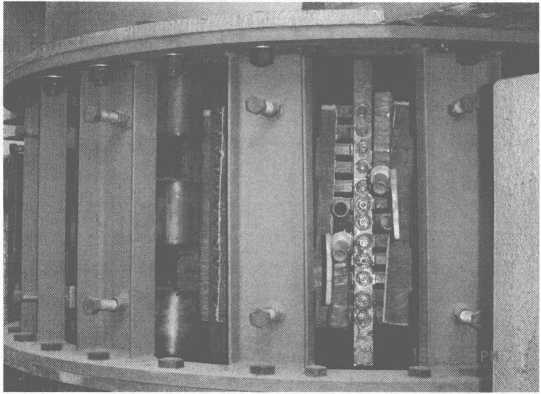 すべての種類のステンレス鋼がバッチ処理された後、クレーン付きの供給タンクから5つの1650t誘導炉にロードされます。 スクラップ鋼を必要な温度(約8°C)に溶かした後、誘導炉内の溶鋼を取鍋に流し込み、使用します。トラックは溶鋼を8t AOD炉に流し込み、そこで脱炭します。スラッギング、脱リン、硫黄除去、合金組成(主にCr、Ni)の調整、次に溶鋼(組成と温度が要件を満たしている)取鍋内の溶鋼を取鍋に入れ、クレーンを使用して注ぐ取鍋内の溶鋼をXNUMXt電磁誘導加熱装置の取鍋に入れます。 保温により加熱されたステンレス鋼液は、横型連続鋳造機で引き抜かれ丸棒に鋳造され、最後に成形・せん断により冷却床に押し込まれます。 。
すべての種類のステンレス鋼がバッチ処理された後、クレーン付きの供給タンクから5つの1650t誘導炉にロードされます。 スクラップ鋼を必要な温度(約8°C)に溶かした後、誘導炉内の溶鋼を取鍋に流し込み、使用します。トラックは溶鋼を8t AOD炉に流し込み、そこで脱炭します。スラッギング、脱リン、硫黄除去、合金組成(主にCr、Ni)の調整、次に溶鋼(組成と温度が要件を満たしている)取鍋内の溶鋼を取鍋に入れ、クレーンを使用して注ぐ取鍋内の溶鋼をXNUMXt電磁誘導加熱装置の取鍋に入れます。 保温により加熱されたステンレス鋼液は、横型連続鋳造機で引き抜かれ丸棒に鋳造され、最後に成形・せん断により冷却床に押し込まれます。 。
図8-10に、8t電磁誘導加熱装置取鍋の物体を示します。
8tおよび14tのタンディッシュ電磁誘導加熱装置であるタンディッシュ誘導加熱装置は、溶鋼の温度を厳密かつ正確に制御でき(誤差範囲はわずか±5〜6℃)、ビレットの品質を保証します。 また、タンディッシュの温度調整時間も適切に延長できるため、誘導加熱装置の効果が良好です。
2アーク連続鋳造機の誘導加熱装置のタンディッシュ装置
アーク連続鋳造機の誘導加熱装置のタンディッシュ装置を図10-9に示します。
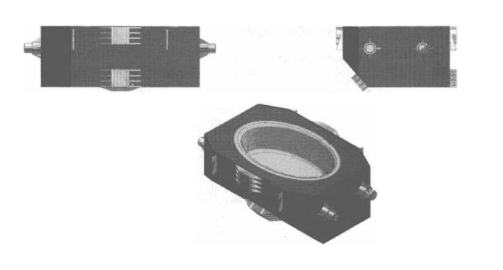
アークビレット連続鋳造機が電磁誘導加熱装置タンディッシュを採用した後、タッピング温度を下げることができます(たとえば、
図10-9アーク連続鋳造機の誘導加熱装置のタンディッシュ装置
1700°Cから1650°C)は、製鋼炉のライニング(コンバーター、電気アーク炉、誘導炉)の寿命を延ばすだけでなく、連続鋳造での溶鋼の温度を安定させ、連続鋳造の品質を保証します。ビレットの鋳造。
以上のことから、連続鋳造タンディッシュ磁気誘導加熱装置は、新しい省エネで環境にやさしい技術であると考えられます。 このデバイスの採用は、冶金企業にとって比較的理想的な技術変革プロジェクトであり、宣伝して使用する価値があります。
図10-10に、16トンのタンディッシュ電磁誘導加熱装置を示します。
図10-10tタンディッシュ電磁誘導加熱装置
図10-11は、14t誘導加熱装置のタンディッシュの概略図です。
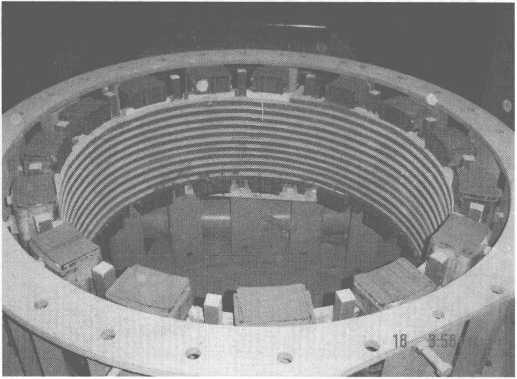
図10-11t誘導加熱装置のタンディッシュの概略図