- 23
- May
Continuous casting tundish molten steel induction heating equipment
Continuous casting tundish molten steel induction heating equipment
1 Overview
Tundish molten steel induction heating equipment technology is developed with the progress of continuous casting technology, the improvement of steel quality requirements, the need for energy saving and consumption reduction, and the matching of external refining and continuous casting processes. Different steel grades have different requirements on the AT of molten steel superheat. For thick plates, in order to reduce internal cracks and loose center, the AT should be low (5~200T); for cold-rolled thin plates, the surface is required to have good quality. Higher (15~300℃). However, the molten steel superheat must be stabilized within a certain range to minimize fluctuations. This is a necessary condition to ensure the smooth progress of continuous casting production, prevent nozzle blockage or prevent leaking accidents, and ensure the quality of cast slabs. The enhancement of the heating function of the tundish makes it possible to control the superheat of molten steel stably. The temperature of the molten steel of different ladle fluctuates, which has an adverse effect on the continuous casting process, and the heating of the tundish can compensate for it to some extent. However, it must be pointed out that maintaining a stable molten steel superheat mainly depends on the proper tapping temperature and the adjustment structure after tapping, and the tundish heating can only play a supplementary role. Nevertheless, the heating and control of molten steel in the tundish is still receiving attention from the metallurgical community. Some countries represented by Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and France have successively carried out research on tundish molten steel heating technology from the 1970s to the 1980s. Japan’s Kawasaki Company first developed and obtained a Japanese patent as early as 1982. At present, the tundish molten steel heating technology successfully developed or under development usually adopts the physical heating method. In the physical heating method, electric energy is used as the heat source and converted according to the electric energy. Different mechanisms can be divided into: electromagnetic induction heating equipment, plasma heating, electroslag heating and DC ceramic heating technology.
Tundish induction heating equipment has the following characteristics:
(1) Fast heating speed and high electric heating efficiency;
(2) Some types also have a certain electromagnetic stirring effect, which is conducive to the removal of inclusions;
(3) The process temperature is easy to control, and the most important thing is to more accurately control the superheat of the molten steel;
(4) The heating power is limited by the depth of the tundish liquid level. Only when the molten steel in the tundish accumulates to a certain depth, the heating can proceed smoothly.
There are several types of tundish induction heating equipment:
(1) According to the type of inductor, it can be divided into coreless induction heating equipment and cored induction heating equipment;
(2) According to the structure of the inductor, it can be divided into increased fault type and tunnel type (groove, molten trench) induction heating equipment;
(3) According to the heating part, it can be divided into local heating and overall heating.
2 Continuous casting tundish molten steel electromagnetic induction heating equipment device
2. 1 Tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment matched with horizontal continuous casting machine
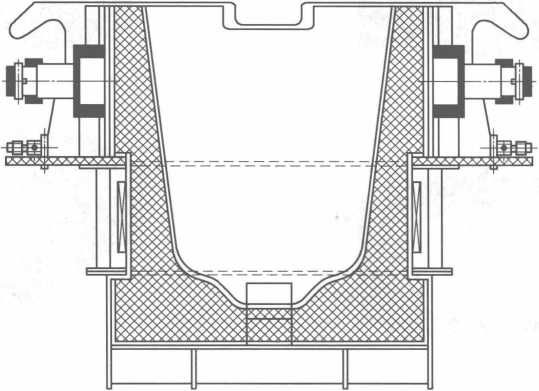
The tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment matched with the horizontal continuous casting machine is shown in Figure 10-7.
The production process of a stainless steel plant is now explained.

Figure 10-7 Tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment matched with horizontal continuous casting machine
 After all kinds of stainless steel are batched, they are loaded into three 5t induction furnaces from the feeding tank with cranes. After the scrap steel is melted to the required temperature (about 1650°C), the molten steel in the induction furnace is poured into the ladle, and then used The truck pours the molten steel into the 8t AOD furnace, where it undergoes decarburization, slagging, dephosphorization and sulfur removal, and adjustment of the alloy composition (mainly Cr, Ni), and then the molten steel (the composition and temperature meet the requirements) Put the molten steel in the ladle into the ladle and use the crane to pour the molten steel in the ladle into the ladle of the 8t electromagnetic induction heating equipment. The stainless steel liquid heated by heat preservation is drawn and casted into a round bar by a horizontal continuous casting machine and finally pushed into the cooling bed by forming and shearing. .
After all kinds of stainless steel are batched, they are loaded into three 5t induction furnaces from the feeding tank with cranes. After the scrap steel is melted to the required temperature (about 1650°C), the molten steel in the induction furnace is poured into the ladle, and then used The truck pours the molten steel into the 8t AOD furnace, where it undergoes decarburization, slagging, dephosphorization and sulfur removal, and adjustment of the alloy composition (mainly Cr, Ni), and then the molten steel (the composition and temperature meet the requirements) Put the molten steel in the ladle into the ladle and use the crane to pour the molten steel in the ladle into the ladle of the 8t electromagnetic induction heating equipment. The stainless steel liquid heated by heat preservation is drawn and casted into a round bar by a horizontal continuous casting machine and finally pushed into the cooling bed by forming and shearing. .
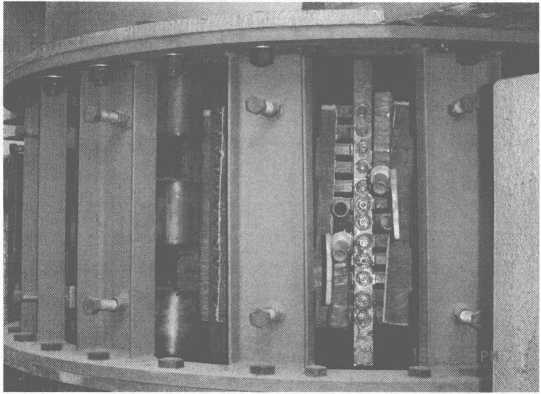
The physical object of the 8t electromagnetic induction heating equipment ladle is shown in Figure 10-8.
8t and 14t tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment, the tundish induction heating equipment can strictly and accurately control the temperature of the molten steel (the error range is only ±5~6℃), thus ensuring the quality of the billet. In addition, the temperature adjustment time of the tundish can also be appropriately extended, showing the good effect of induction heating equipment.
2. 2 Tundish device of induction heating equipment of arc continuous casting machine
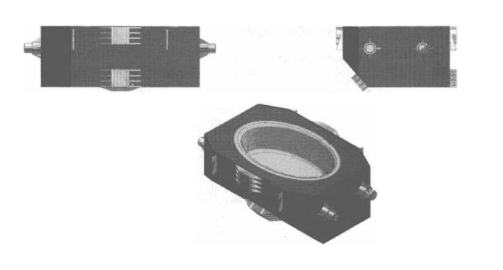
The tundish device of the induction heating equipment of the arc continuous casting machine is shown in Figure 10-9.
After the arc billet continuous caster adopts the electromagnetic induction heating equipment tundish, the tapping temperature can be lowered (for example, it can be
Figure 10-9 Tundish device of induction heating equipment of arc continuous casting machine
From 1700°C to 1650°C), this not only helps to improve the life of steelmaking furnace lining (converter, electric arc furnace or induction furnace), but also stabilizes the temperature of molten steel in continuous casting and guarantees the quality of continuous casting billets.
Based on the above introduction, it can be considered that the continuous casting tundish magnetic induction heating equipment is a new energy-saving and environmentally-friendly technology. The adoption of this device is a relatively ideal technological transformation project for metallurgical enterprises, and it is worthy of promotion and use.
Figure 10-10 shows the 16t tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment.
Figure 10-10 16t tundish electromagnetic induction heating equipment
Figure 10-11 is a schematic diagram of the tundish of 14t induction heating equipment.
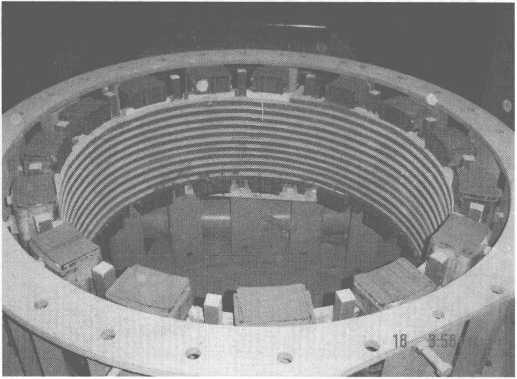
Figure 10-11 Schematic diagram of the tundish of 14t induction heating equipment